1. Understanding the Role of the Colon in Health
Before discussing the specific supplements, it’s important to understand the critical functions of the colon and how it impacts overall health.
1.1 The Function of the Colon
- Digestion and Absorption: The colon is responsible for absorbing water and electrolytes, transforming undigested food into stool, and maintaining the balance of gut bacteria.
- Gut Microbiota: The colon is home to trillions of microorganisms (gut microbiota) that help break down food, synthesize vitamins, and support immune function.
- Waste Elimination: The colon plays an essential role in eliminating waste products from the body.
1.2 Common Colon Health Issues
- Constipation: Slow-moving stool due to poor motility.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): A disorder affecting bowel movements, causing symptoms like bloating, diarrhea, or constipation.
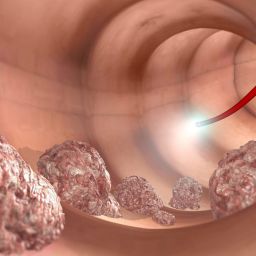
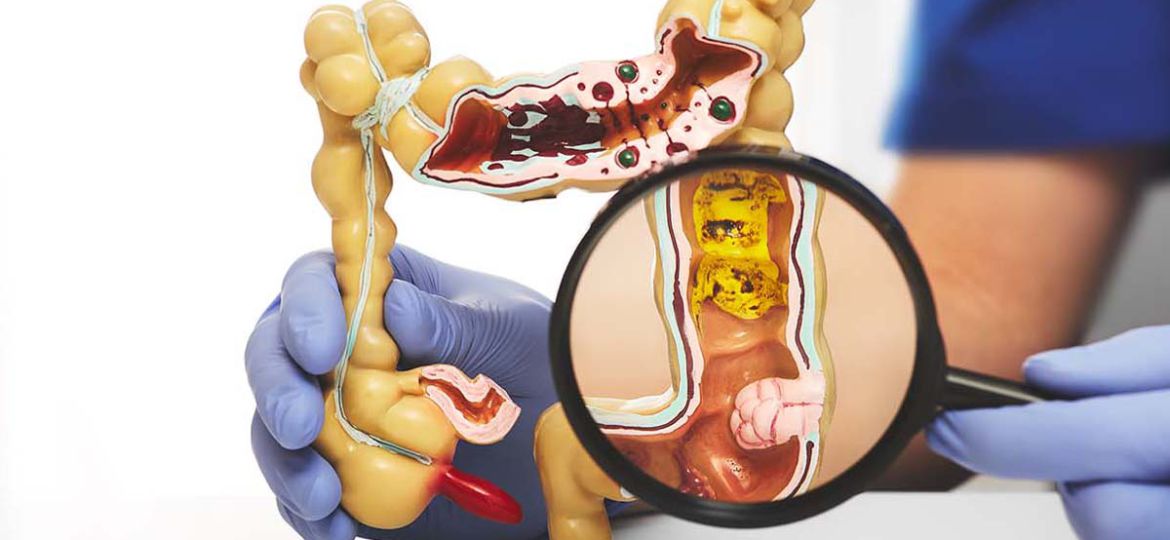
- Colorectal Cancer: A major health concern related to inflammation, diet, and genetic predisposition.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, which cause chronic inflammation of the digestive tract.
2. Key Supplements for Colon Health
Many supplements are marketed for colon health, but not all have proven efficacy. Below are the supplements with the most scientific backing in supporting colon health.
2.1 Probiotics
- What Are Probiotics?: Probiotics are live beneficial bacteria that help restore or improve the balance of gut microbiota.
- How Probiotics Support Colon Health:
- Gut Flora Balance: Probiotics help to maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria, which is vital for digestion, immune health, and preventing the overgrowth of harmful bacteria.
- Reducing Inflammation: Probiotics have been shown to reduce inflammation in the colon, which can help manage conditions like IBS, IBD, and diverticulitis.
- Improving Bowel Movements: Certain probiotic strains, such as Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus, may improve stool regularity and reduce symptoms of constipation.
2.2 Fiber Supplements
- The Importance of Fiber: Fiber is essential for regular bowel movements and colon health. It adds bulk to the stool and promotes peristalsis (the wave-like motion that moves stool through the digestive tract).
- Types of Fiber Supplements:
- Soluble Fiber: Found in products like psyllium husk and inulin, soluble fiber dissolves in water and forms a gel-like substance, which can help soften stool and improve its passage through the colon.
- Insoluble Fiber: Found in wheat bran and cellulose, this type of fiber helps add bulk to stool, making it easier to pass and promoting regularity.
- Health Benefits of Fiber:
- Preventing Constipation: Fiber is known for its ability to prevent and relieve constipation.
- Supporting Gut Health: Fiber supports healthy gut microbiota by serving as a food source for beneficial bacteria.
- Reducing Colon Cancer Risk: High-fiber diets are linked to a lower risk of colorectal cancer, likely due to fiber’s ability to speed up the passage of food through the colon.
2.3 Omega-3 Fatty Acids
- What Are Omega-3s?: Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats found in fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts.
- Benefits of Omega-3s for Colon Health:
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Omega-3s have strong anti-inflammatory properties, which can benefit individuals with inflammatory bowel diseases like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
- Supporting Gut Health: Omega-3s help maintain the integrity of the colon’s lining, which can prevent conditions like leaky gut syndrome.
- Preventing Colon Cancer: Studies have shown that omega-3 fatty acids may help prevent the growth of colon cancer cells by reducing inflammation.
2.4 Vitamin D
- Vitamin D and Colon Health:
- Regulating Immune Function: Vitamin D plays a crucial role in regulating immune responses, which is particularly important for preventing colon cancer and inflammatory bowel diseases.
- Reducing Colon Cancer Risk: There is evidence that adequate vitamin D levels are associated with a lower risk of developing colorectal cancer. Vitamin D helps modulate the growth and differentiation of colon cells, potentially inhibiting tumor formation.
2.5 Antioxidants: Vitamin C, E, and Selenium
- The Role of Antioxidants: Antioxidants help neutralize harmful free radicals that can damage colon cells and increase the risk of colorectal cancer.
- Vitamin C and E:
- Supporting Immune Health: These vitamins enhance immune responses and protect the colon cells from oxidative stress and DNA damage.
- Cancer Prevention: Several studies have suggested that antioxidant-rich diets may reduce the risk of colorectal cancer.
- Selenium:
- Antioxidant Power: Selenium is a mineral with powerful antioxidant properties that may help protect colon cells from damage caused by oxidative stress.
2.6 Curcumin
- What Is Curcumin?: Curcumin is the active compound in turmeric, known for its potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
- Benefits for Colon Health:
- Reducing Inflammation: Curcumin may reduce inflammation in the colon, making it beneficial for individuals with inflammatory bowel diseases.
- Preventing Colon Cancer: Some studies suggest that curcumin may help prevent the growth of cancerous cells in the colon by interfering with cancer cell proliferation and promoting apoptosis (programmed cell death).
3. The Role of a Balanced Diet in Colon Health
While supplements can play an important role in supporting colon health, they should complement a balanced diet. A diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats is essential for maintaining optimal digestive function. In addition to fiber, foods rich in polyphenols, antioxidants, and prebiotics (such as garlic, onions, and bananas) can promote gut health.
4. Considerations and Potential Risks of Supplements
While supplements can be beneficial, they should be used with caution. It’s essential to:
- Consult a Healthcare Provider: Always consult a healthcare provider before starting a supplement regimen, especially if you have underlying health conditions or take other medications.
- Avoid Overuse: Taking excessive amounts of certain supplements, such as fiber or omega-3s, can lead to side effects like bloating, diarrhea, or nutrient imbalances.
Effective Supplements for Colon Health
Maintaining colon health is essential for overall well-being, particularly as we age. The supplements mentioned—probiotics, fiber, omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, antioxidants, and curcumin—can play a significant role in supporting colon function, reducing inflammation, and potentially lowering the risk of colon cancer. However, supplements should always be used in conjunction with a healthy diet and lifestyle to achieve the best results.
By understanding the science behind these supplements and how they contribute to colon health, individuals can make informed decisions about which ones are right for their needs. As always, consulting with a healthcare professional is key to ensuring safe and effective use.