How Does Bile Duct Stricture Impact Liver Function?
The narrowing of the bile ducts directly impacts liver function because the liver is responsible for producing bile, which is essential for digestion. Bile duct stricture interferes with the transport of bile from the liver to the intestines, leading to the following complications:
1. Bile Accumulation in the Liver
When the bile ducts become narrowed or blocked, bile cannot flow from the liver to the small intestine. As a result, bile accumulates in the liver. This condition is called cholestasis, and it can cause the liver cells to become damaged due to the increased pressure from the buildup of bile. Over time, this can result in liver inflammation, fibrosis (scarring), and eventually cirrhosis if the bile duct stricture is left untreated.
2. Jaundice and Elevated Bilirubin Levels
One of the key consequences of bile duct stricture is the accumulation of bilirubin, a waste product produced when red blood cells are broken down. Normally, bilirubin is excreted through bile into the intestines. However, when bile cannot flow properly due to a bile duct obstruction, bilirubin backs up into the bloodstream, leading to jaundice—a condition in which the skin and the whites of the eyes turn yellow.
Increased levels of bilirubin in the bloodstream can also cause other symptoms, including dark urine and pale stools. These signs often indicate an underlying issue with bile flow, such as a bile duct stricture.
3. Fat Malabsorption and Digestive Issues
Bile plays a crucial role in the digestion of fats and fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E, and K). When bile flow is impaired due to a bile duct stricture, fat digestion is hindered, leading to fat malabsorption. This condition can cause a variety of digestive problems, including:
- Steatorrhea: The presence of fatty, pale, and foul-smelling stools due to undigested fats.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Difficulty digesting fatty foods can lead to digestive discomfort and nausea.
- Weight Loss: Chronic malabsorption of nutrients can result in unintentional weight loss, as the body is unable to absorb essential nutrients effectively.
4. Liver Damage and Fibrosis
If bile duct stricture is left untreated, the prolonged buildup of bile can cause damage to liver cells. The increased pressure from bile accumulation leads to liver inflammation and fibrosis, where healthy liver tissue is replaced with scar tissue. Over time, this can result in cirrhosis, a severe liver condition that can cause liver failure. In advanced stages, cirrhosis may require a liver transplant.
Causes of Bile Duct Stricture and Its Impact on Liver Function
Bile duct stricture can occur due to several conditions, some of which are benign, while others are more serious and may lead to liver dysfunction. The following are some of the most common causes of bile duct stricture:
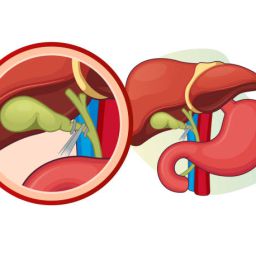
1. Gallstones and Bile Duct Stones
One of the most common causes of bile duct stricture is the presence of gallstones or bile duct stones. Gallstones are solid particles that can form in the gallbladder and sometimes travel into the bile ducts, causing a blockage. The blockage can lead to bile duct inflammation, scarring, and narrowing, ultimately resulting in a stricture. Gallstones can cause temporary or long-term bile duct obstruction, depending on the severity of the blockage.
2. Bile Duct Injury from Surgery or Trauma

Bile duct injury during surgical procedures involving the gallbladder, liver, or bile ducts can result in scarring and narrowing of the ducts. Cholecystectomy, the surgical removal of the gallbladder, is one of the most common procedures that may result in bile duct injury. If the bile duct is not repaired properly following an injury, it can develop a stricture, obstructing bile flow and impairing liver function.
Injury to the bile ducts may also occur as a result of trauma or infections.
3. Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC)
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a chronic disease that causes inflammation and scarring of the bile ducts. PSC often occurs in individuals with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), particularly ulcerative colitis. Over time, the inflammation causes the bile ducts to narrow, leading to cholestasis and liver dysfunction. PSC can progress to liver cirrhosis and liver failure if not properly managed.
4. Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer)
Cholangiocarcinoma is a rare form of cancer that originates in the bile ducts. As the tumor grows, it can obstruct bile flow, leading to bile duct stricture. Cholangiocarcinoma can be difficult to detect in the early stages, and it often presents with symptoms such as jaundice, abdominal pain, and weight loss. If left untreated, it can severely impair liver function and lead to liver failure.
5. Autoimmune Conditions
Autoimmune diseases such as autoimmune cholangitis and autoimmune hepatitis can also cause bile duct stricture. In these conditions, the immune system mistakenly attacks the bile ducts, leading to inflammation and scarring. These autoimmune conditions can result in progressive liver damage, making it essential to manage the underlying autoimmune response with medications.
Diagnosis of Bile Duct Stricture
Diagnosing bile duct stricture involves several steps, including a combination of medical history, physical examinations, imaging tests, and laboratory tests. Key diagnostic methods include:
- Blood Tests: Elevated liver enzymes, bilirubin levels, and other markers can indicate impaired liver function and bile duct obstruction.
- Ultrasound: An ultrasound of the liver and bile ducts can reveal blockages or narrowing of the bile ducts.
- Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): ERCP is a specialized imaging technique that allows healthcare providers to visualize the bile ducts and, if necessary, perform procedures such as stone removal or stent placement.
- Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP): MRCP is a non-invasive imaging method that can provide detailed images of the bile ducts and detect any strictures or blockages.
- Liver Biopsy: In some cases, a liver biopsy may be performed to assess the extent of liver damage and identify underlying conditions like PSC or liver cancer.
Treatment of Bile Duct Stricture
The treatment of bile duct stricture depends on its underlying cause and severity. The following are common treatment options:
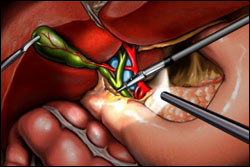
1. Endoscopic Procedures
- Balloon Dilation: This procedure involves inflating a balloon inside the narrowed bile duct to widen the stricture and restore bile flow.
- Stent Placement: In some cases, a stent (a small tube) may be placed in the bile duct to keep it open and maintain bile flow.
2. Surgery
In more severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair the stricture, remove obstructions, or bypass the blocked bile ducts.
3. Medical Management
For conditions like PSC, autoimmune diseases, or cholangiocarcinoma, medications such as immunosuppressants or chemotherapy may be used to manage the underlying condition.
Bile duct stricture is a significant condition that can impair liver function and affect overall digestive health. The narrowing or obstruction of the bile ducts leads to bile accumulation in the liver, causing jaundice, digestive issues, and liver damage. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent serious complications, including liver cirrhosis and liver failure. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for bile duct stricture, individuals can work with healthcare providers to manage the condition effectively and improve their quality of life.