1. Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC)
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is one of the most common causes of bile duct stricture. PSC is a chronic, progressive autoimmune disease that causes inflammation and scarring (fibrosis) of the bile ducts. The cause of PSC is not entirely understood, but it is believed to be linked to an immune system attack on the bile ducts. It often occurs in people with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), particularly those with ulcerative colitis.
How PSC Leads to Bile Duct Stricture
In PSC, the bile ducts become inflamed, and over time, they develop fibrous tissue that causes narrowing (stricture) of the ducts. This fibrosis disrupts bile flow, leading to cholestasis, which can result in jaundice, itching, and liver damage. As the disease progresses, the bile ducts may become completely blocked, leading to liver failure.
Symptoms of PSC
- Fatigue
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Abdominal pain
- Itchy skin (pruritus)
- Dark urine and light-colored stools
PSC is a progressive disease, and over time, it can lead to cirrhosis and increase the risk of liver cancer. Treatment is focused on managing symptoms and slowing disease progression, as there is no definitive cure for PSC.
2. Chronic Cholangitis
Chronic cholangitis is a long-term inflammation of the bile ducts, which can lead to scarring and narrowing of the ducts. It is most commonly caused by repeated episodes of acute cholangitis, which is a bacterial infection of the bile ducts. Chronic cholangitis can also be linked to conditions like gallstones, bile duct tumors, or other obstructions in the bile duct system.
How Chronic Cholangitis Causes Stricture
Repeated infections or long-standing inflammation can cause fibrosis and scarring of the bile ducts, resulting in strictures. The inflammation can also damage the inner lining of the bile ducts, making them more prone to infection and further scarring.
Symptoms of Chronic Cholangitis
- Fever and chills (especially during infection flare-ups)
- Jaundice
- Abdominal pain, especially in the upper right side
- Fatigue and weakness
- Nausea and vomiting
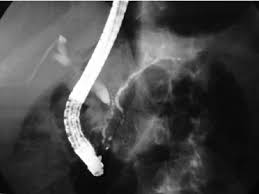
Chronic cholangitis is often treated with antibiotics to manage infections and procedures like endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) or surgical interventions to remove blockages or place stents to restore bile flow.
3. Bile Duct Injury After Surgery
Surgical procedures involving the bile ducts, gallbladder, or liver, such as gallbladder removal (cholecystectomy), can lead to injury or trauma to the bile ducts. These injuries may cause bile duct narrowing or stricture, especially if the ducts are accidentally cut, ligated, or otherwise damaged during surgery.
How Surgery Leads to Stricture
Bile duct injury during surgery can cause inflammation and scarring in the affected area, leading to a narrowing or complete blockage of the bile duct. This can obstruct bile flow and result in the accumulation of bile in the liver, causing jaundice and other complications.
Symptoms of Bile Duct Injury
- Pain in the upper right abdomen
- Jaundice
- Fever and chills (if an infection occurs)
- Vomiting and nausea
- Dark urine and light-colored stools
Surgical repair or procedures such as ERCP or stent placement are commonly used to manage bile duct injury and restore bile flow.
4. Gallstones
Gallstones are hardened deposits of bile that can form in the gallbladder. If a gallstone becomes lodged in the bile duct, it can block bile flow, causing inflammation and infection in the bile ducts. This condition is known as biliary colic or acute cholangitis when it causes infection.
How Gallstones Lead to Bile Duct Stricture
If a gallstone causes a blockage in the bile duct, it can trigger an infection (cholangitis) or long-term inflammation. Chronic inflammation from recurrent infections can lead to scarring and the development of bile duct strictures. Over time, the repeated obstruction and inflammation can lead to further damage and narrowing of the ducts.
Symptoms of Gallstones Causing Stricture
- Severe upper abdominal pain (especially after meals)
- Nausea and vomiting
- Jaundice
- Dark urine and pale stools
- Fever (if infection occurs)
The treatment for gallstones causing bile duct stricture often involves removing the gallstones through surgery or using ERCP to remove the stones and place stents to allow bile flow.
5. Pancreatic Cancer or Pancreatitis
Pancreatic cancer, particularly tumors located near the bile ducts, can cause bile duct obstruction and lead to strictures. Similarly, pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas) can cause inflammation in the bile ducts and lead to scarring and narrowing over time.
How Pancreatic Cancer or Pancreatitis Causes Stricture
Tumors in the pancreas or bile ducts can directly block bile ducts, leading to the development of strictures. Inflammation associated with pancreatitis can also lead to scarring in the bile ducts, narrowing the ducts and causing a buildup of bile.
Symptoms of Pancreatic Cancer or Pancreatitis Causing Stricture
- Jaundice
- Unexplained weight loss
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue and weakness
Treatment for bile duct stricture caused by pancreatic conditions may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or surgery to remove the tumor or manage the stricture.
6. Bile Duct Cysts (Choledochal Cysts)
Bile duct cysts, also known as choledochal cysts, are congenital abnormalities of the bile ducts. These cysts can cause blockages or inflammation in the bile ducts, leading to the development of strictures over time. The cysts may become infected, further contributing to bile duct narrowing and damage.
How Bile Duct Cysts Cause Stricture
Bile duct cysts can disrupt the normal flow of bile and cause pressure buildup within the bile ducts. If left untreated, the cysts can become infected or cause scarring in the surrounding bile duct tissue, leading to narrowing or stricture.
Symptoms of Bile Duct Cysts
- Jaundice
- Abdominal pain (especially after eating)
- Fever (if infection occurs)
- Nausea and vomiting
Treatment for choledochal cysts typically involves surgical removal of the cyst and repair of the affected bile ducts. If a stricture has already developed, procedures such as ERCP or surgery may be necessary.
7. Tuberculosis (TB)
In rare cases, tuberculosis (TB), a bacterial infection primarily affecting the lungs, can spread to the bile ducts and cause inflammation. TB infections in the bile ducts are known as biliary tuberculosis and can result in the formation of strictures over time.
How TB Causes Stricture
Biliary tuberculosis can cause scarring and narrowing of the bile ducts due to chronic inflammation. TB infections in the bile ducts can also lead to complications such as cholangitis, which may further damage the ducts.
Symptoms of Biliary Tuberculosis
- Jaundice
- Abdominal pain
- Weight loss and fever (common with TB infections)
- Night sweats
- Loss of appetite
Treatment for biliary tuberculosis typically involves a course of antibiotics to treat the TB infection. If strictures are present, procedures such as stent placement may be required.
Bile duct stricture is a serious condition that can arise from a variety of diseases, including autoimmune conditions like primary sclerosing cholangitis, infections, surgical injuries, and even cancer. Identifying the underlying cause of bile duct stricture is critical for effective treatment. Early diagnosis and intervention can help prevent further damage to the bile ducts, liver, and digestive system. Treatment may involve medications, surgical procedures, and in some cases, liver transplantation for advanced cases. Understanding the relationship between these diseases and bile duct stricture can guide healthcare providers in offering better management strategies and improving patient outcomes.