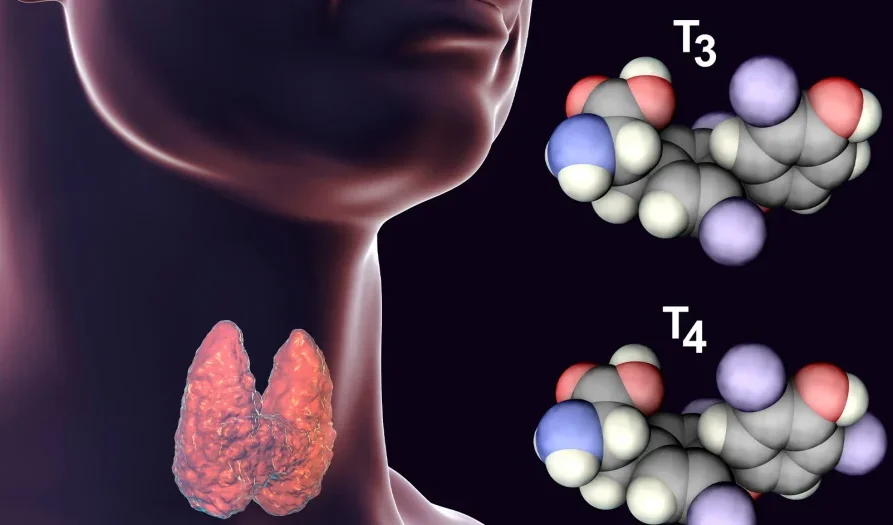
1. Increased Heart Rate and Palpitations
One of the most noticeable effects of excess thyroid hormones is the acceleration of the heart rate. The thyroid hormones directly influence the heart’s electrical system, leading to an increased number of heartbeats per minute. This condition is known as tachycardia. Individuals with hyperthyroidism often experience heart palpitations, which are sudden, irregular heartbeats that can feel like the heart is pounding or fluttering.
The increased heart rate puts additional strain on the heart, as it needs to work harder to pump blood throughout the body. Over time, this can lead to complications, such as atrial fibrillation (AFib), a type of arrhythmia that can increase the risk of stroke and other cardiovascular issues.
2. Increased Metabolism and Weight Loss
Excess thyroid hormones can lead to an acceleration of metabolism, which increases the rate at which the body burns calories. This results in a higher energy expenditure, which often leads to unexplained weight loss. Despite having a normal or even increased appetite, individuals with hyperthyroidism may find that they are losing weight rapidly.
The increased metabolic rate also leads to an increased demand for oxygen and energy in the body, which may result in feelings of weakness and fatigue despite the high energy expenditure. As the body works harder to meet this demand, the muscles may begin to weaken, causing muscle wasting in severe cases of hyperthyroidism.
3. Heat Intolerance and Sweating
Since thyroid hormones regulate the body’s temperature, an overproduction of these hormones leads to heat intolerance. People with hyperthyroidism often feel excessively hot, even in cool environments. This is because the accelerated metabolism leads to increased heat production.
As a result, individuals may experience excessive sweating, even without engaging in physical activity. This can lead to dehydration if the body loses too much fluid, further contributing to feelings of fatigue and weakness.
4. Nervousness, Anxiety, and Irritability
Excess thyroid hormones also affect the nervous system, leading to changes in mood and behavior. People with hyperthyroidism often experience feelings of nervousness, anxiety, and irritability. The overstimulation of the central nervous system due to high thyroid hormone levels can lead to hyperactivity, restlessness, and difficulty concentrating.
In more severe cases, hyperthyroidism can cause panic attacks, insomnia, and even psychosis. These changes in mood and mental health are often some of the first signs of thyroid dysfunction and can significantly impact a person’s quality of life.
5. Gastrointestinal Changes: Diarrhea and Increased Bowel Movements
Excess thyroid hormones also have a profound impact on the digestive system. People with hyperthyroidism often experience more frequent and urgent bowel movements, sometimes leading to diarrhea. This is because thyroid hormones help regulate the motility of the intestines, speeding up the movement of food and waste through the gastrointestinal tract.
The increased bowel movement frequency can lead to dehydration and electrolyte imbalances, which can further exacerbate the physical symptoms of hyperthyroidism, such as fatigue and muscle weakness.
6. Muscle Weakness and Tremors

Another common effect of excess thyroid hormones is muscle weakness, particularly in the upper arms and thighs. The accelerated metabolism leads to muscle protein breakdown, resulting in reduced muscle strength. This can make physical tasks more difficult and may lead to a feeling of fatigue or heaviness.
In addition to muscle weakness, individuals with hyperthyroidism often experience fine hand tremors. These tremors are typically subtle but can become more noticeable when a person is attempting to hold something steady. The tremors result from the overstimulation of the muscles by the excess thyroid hormones.
7. Sleep Disturbances and Insomnia
The overstimulation of the nervous system caused by high levels of thyroid hormones can also lead to sleep disturbances. People with hyperthyroidism often find it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep, experiencing insomnia. The body’s heightened metabolism and constant state of “alertness” make it challenging for the body to relax and rest, even after a long day.
Chronic sleep deprivation can further worsen the symptoms of hyperthyroidism, including fatigue, mood changes, and difficulty concentrating. It may also have long-term effects on cardiovascular health, as inadequate sleep can increase the risk of high blood pressure and heart disease.
8. Menstrual Irregularities
In women, one of the effects of excess thyroid hormones can be menstrual irregularities. Hyperthyroidism can lead to lighter or less frequent periods, and in some cases, menstruation may stop altogether. This occurs because thyroid hormones play a key role in regulating the hormonal balance that governs the menstrual cycle.
Irregular periods or the absence of menstruation can be an early indicator of thyroid dysfunction and should be assessed by a healthcare provider. If left untreated, these hormonal imbalances can affect fertility and lead to additional complications.
9. Eye Issues: Bulging Eyes and Dryness
In some cases of hyperthyroidism, particularly Graves’ disease, individuals may experience eye problems, including exophthalmos (bulging eyes) and dryness. Graves’ disease is an autoimmune disorder that causes the body’s immune system to attack the thyroid, often resulting in an overproduction of thyroid hormones. The immune response can also affect the tissues around the eyes, causing inflammation and bulging.
These eye symptoms can be severe, leading to discomfort, vision problems, and even damage to the eyes in extreme cases. Prompt treatment of hyperthyroidism can help manage these symptoms and prevent long-term eye damage.
Managing Excess Thyroid Hormones
Excess thyroid hormones, or hyperthyroidism, can cause significant changes in the body, affecting multiple systems from the cardiovascular and digestive systems to the nervous system and reproductive health. The key changes that occur, including increased heart rate, weight loss, anxiety, and muscle weakness, can have a profound impact on daily life and overall well-being.
The good news is that with proper diagnosis and treatment, hyperthyroidism can be managed effectively. Treatment options include medications (such as beta-blockers and antithyroid drugs), radioactive iodine therapy, and sometimes surgery to remove part of the thyroid gland. Regular monitoring and early intervention are crucial to managing the condition and preventing long-term health complications.
If you suspect you have hyperthyroidism or are experiencing any of the symptoms mentioned in this article, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider who can assess your thyroid function and recommend the appropriate course of treatment. With timely medical attention, individuals with hyperthyroidism can lead healthy, balanced lives.