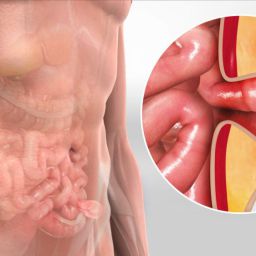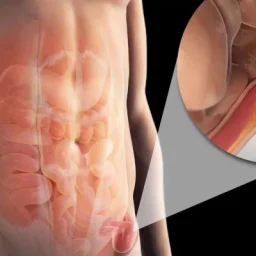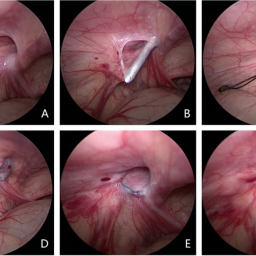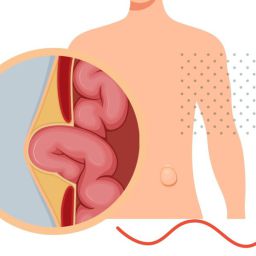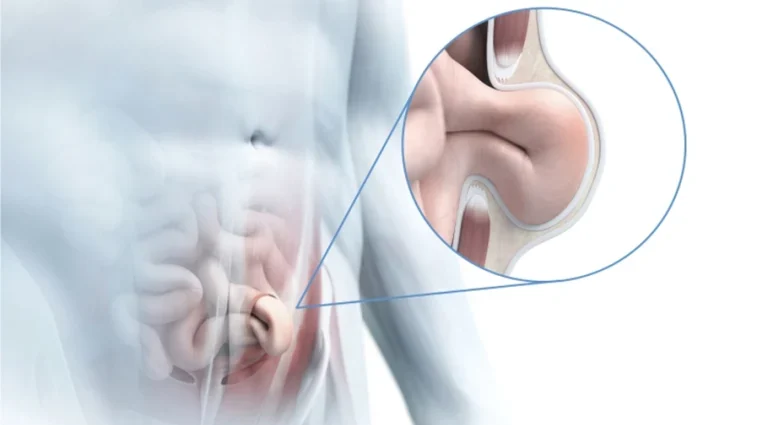
1. Rest and Avoiding Strain
One of the simplest and most effective home treatment methods for managing an inguinal hernia is rest and minimizing physical strain. Hernias are often exacerbated by activities that increase abdominal pressure, such as heavy lifting, intense physical exercise, or straining during bowel movements.
- Rest: Resting and avoiding strenuous activities can prevent further strain on the weakened abdominal wall, which may prevent the hernia from getting worse. Lying down or avoiding heavy physical activities can reduce discomfort and limit the risk of complications.
- Avoiding Physical Strain: It’s essential to avoid activities that may worsen the hernia, such as lifting heavy objects, bending over excessively, or engaging in high-intensity exercises that stress the core muscles. This approach helps prevent unnecessary pressure on the hernia and supports healing.
2. Use of Hernia Belts or Supports
Hernia belts or supports are commonly used as a home treatment option for people with inguinal hernias. These specially designed garments provide additional support to the abdominal area, which can help alleviate discomfort and prevent the hernia from protruding further.
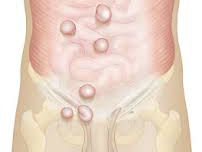
- Hernia Belts: These are elasticated bands or supports that fit around the waist and apply gentle pressure on the hernia. Wearing a hernia belt can help hold the hernia in place, preventing it from bulging out further and reducing the discomfort caused by the hernia.
- Benefits: A hernia belt can provide relief, particularly for people who are waiting for surgery or those who cannot undergo surgery immediately. However, a hernia belt should not be considered a permanent solution—it is a temporary measure to manage symptoms until professional treatment is sought.
3. Dietary Modifications to Prevent Constipation
One of the contributing factors to the development and worsening of inguinal hernias is chronic constipation, which puts pressure on the abdominal wall during bowel movements. Therefore, dietary modifications can play a significant role in alleviating symptoms and preventing further strain on the hernia.
- High-Fiber Diet: Consuming a high-fiber diet can help regulate bowel movements and prevent constipation. Foods such as whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes are rich in fiber and promote healthy digestion.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water throughout the day is essential for maintaining smooth digestion and preventing constipation. Dehydration can lead to hard stools, which increase the effort required during bowel movements and may worsen the hernia.
- Probiotics: Including probiotics in the diet, such as yogurt or fermented foods, may help improve gut health and reduce bloating or discomfort that could put additional pressure on the abdominal area.
4. Exercise and Core Strengthening (with Caution)
While strenuous exercise should be avoided with an inguinal hernia, certain low-impact activities can help maintain muscle strength and prevent the hernia from worsening. Core strengthening exercises are crucial for supporting the abdominal wall and preventing strain on the hernia site.
- Gentle Core Exercises: Exercises such as pelvic tilts, leg raises, and light abdominal crunches (under the guidance of a healthcare provider) can help strengthen the muscles of the abdomen and reduce pressure on the hernia. It’s essential to perform these exercises with caution and avoid exercises that put undue stress on the groin or abdomen.
- Walking and Light Stretching: Regular walking and gentle stretching can help maintain overall health and prevent muscle atrophy. These low-impact activities do not increase abdominal pressure significantly, making them safe for people with inguinal hernias when done moderately.
- Avoiding High-Impact Activities: Activities such as running, weightlifting, or heavy lifting should be avoided, as they put significant strain on the abdominal muscles, potentially worsening the hernia.
5. Using Cold Compresses or Ice Packs for Pain Relief
In some cases, inguinal hernias can cause discomfort or inflammation in the affected area. Cold therapy can be an effective home remedy for managing pain and reducing swelling associated with a hernia.
- Cold Compresses: Applying an ice pack or cold compress to the hernia site for 15-20 minutes several times a day can help reduce swelling and numb the area, providing temporary relief from pain or discomfort.
- Caution: While cold therapy can be helpful for symptom management, it should be used sparingly. Direct application of ice should be avoided for extended periods, as it may cause skin damage or frostbite. Always wrap the ice pack in a cloth before applying it to the skin.
6. Managing Weight and Avoiding Obesity
Excess weight can place significant strain on the abdominal wall and exacerbate the symptoms of an inguinal hernia. Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the risk of the hernia getting worse and help alleviate pressure on the abdominal muscles.
- Healthy Diet and Portion Control: In addition to a high-fiber diet, adopting a balanced diet that emphasizes portion control and reduces the intake of unhealthy fats, sugars, and processed foods can promote weight loss and prevent obesity, which is a major risk factor for hernias.
- Gradual Weight Loss: If overweight, losing weight gradually through a combination of diet and moderate exercise can relieve excess pressure on the abdominal wall, reducing the likelihood of the hernia worsening.
7. Herbal Remedies and Natural Treatments (with Caution)
Some individuals seek natural or herbal remedies to help manage the symptoms of inguinal hernia. While these remedies may not cure the hernia, certain herbs and natural products may offer symptom relief and improve overall digestive health.
- Ginger and Turmeric: Both ginger and turmeric are known for their anti-inflammatory properties. Consuming these herbs may help reduce swelling and inflammation in the abdominal area.
- Chamomile Tea: Chamomile is known for its soothing properties, and drinking chamomile tea may help reduce gastrointestinal discomfort or bloating, which can contribute to abdominal pressure.
- Caution: Herbal remedies should be used with caution, as they may interact with medications or have side effects. Always consult with a healthcare provider before using herbal treatments, especially for chronic conditions.
8. Avoiding Smoking and Alcohol Consumption
Both smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can negatively affect the body’s ability to heal and may contribute to the worsening of inguinal hernias. Smoking, in particular, is linked to chronic coughing, which can increase abdominal pressure and aggravate hernias.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking cessation can improve lung function and reduce the risk of chronic coughing, which may place additional strain on the abdominal wall. Moreover, quitting smoking enhances overall health and promotes better healing.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol intake can impair liver function and increase the risk of gastrointestinal problems, such as constipation, which could worsen the symptoms of an inguinal hernia. Moderating alcohol consumption is beneficial for overall well-being.
While surgery remains the most effective solution for treating inguinal hernias, there are several home treatment methods that can help manage symptoms and prevent the condition from worsening. Rest, dietary changes, proper use of hernia belts, and certain exercises can provide relief for individuals living with a hernia. However, these methods are not substitutes for professional medical treatment, and individuals with hernias should consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of action.
It’s important to remember that a hernia will not heal on its own without intervention. Home treatments can only offer temporary relief or support, and individuals should be proactive in seeking medical advice when necessary. With the right combination of home care and professional medical intervention, most individuals with inguinal hernias can manage their condition effectively and improve their quality of life.