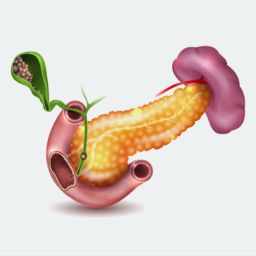
Treatment Options for Gallbladder Cancer
Treatment for gallbladder cancer usually involves a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy, depending on the stage and spread of the disease.
- Surgery: If the cancer is detected early and is localized to the gallbladder, surgery to remove the gallbladder (cholecystectomy) may be performed. In more advanced cases, other nearby tissues and organs may also need to be removed.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy is often used when the cancer has spread beyond the gallbladder. It involves the use of drugs that kill cancer cells or slow their growth.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to target and destroy cancer cells. This may be used in conjunction with surgery or chemotherapy.
While these treatments are essential for combating gallbladder cancer, they can cause side effects that affect the body’s nutritional needs. Chemotherapy, for example, may lead to nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite, while radiation may cause fatigue and digestive issues. This makes nutritional support a crucial component of cancer care.
The Role of Nutrition in Cancer Treatment
Nutrition plays several important roles during cancer treatment and recovery. It helps maintain strength and energy, supports the immune system, minimizes treatment side effects, and aids in tissue repair and healing. A well-balanced diet can also improve mood and overall well-being, both of which are essential for the emotional and physical healing process.
Enhancing the Immune System
A healthy immune system is essential for fighting cancer and preventing infections, especially during treatment. Certain nutrients, such as vitamins A, C, D, E, and zinc, play a critical role in strengthening immune defenses. Adequate protein intake is also important for immune function and tissue repair, as it supports the production of immune cells and antibodies.
Managing Treatment Side Effects
Cancer treatments such as chemotherapy and radiation often cause side effects that can affect appetite, digestion, and overall health. For example:
- Nausea and Vomiting: Common side effects of chemotherapy that can lead to dehydration and malnutrition.
- Loss of Appetite: Treatment-induced fatigue and changes in taste can result in reduced food intake.
- Diarrhea or Constipation: Digestive issues are often experienced during cancer treatments and can affect nutrient absorption.
A carefully planned diet can help mitigate these side effects and prevent nutritional deficiencies that can impair healing and recovery.
Supporting Healing and Tissue Repair
Cancer treatments, particularly surgery and chemotherapy, can cause damage to healthy tissues. Protein and specific vitamins and minerals are essential for tissue repair. Foods rich in protein, as well as vitamin C and zinc, can support the regeneration of cells and tissues, helping the body recover more quickly from the damage caused by treatments.
Key Nutrients for Gallbladder Cancer Patients
Certain nutrients are particularly important during the treatment of gallbladder cancer. These nutrients help manage side effects, support healing, and provide the energy necessary for the body to combat cancer.
1. Protein
Protein is essential for healing, especially when undergoing cancer treatments that may damage muscle tissue. It helps repair and regenerate cells, boost the immune system, and maintain strength. Sources of protein include lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, legumes, tofu, and low-fat dairy products.
2. Healthy Fats
Fat is an essential nutrient that provides long-lasting energy and helps in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E, and K. Gallbladder cancer patients, particularly those who have undergone surgery or whose gallbladder is no longer functioning, may have difficulty digesting fats. Therefore, it is important to choose healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, olive oil, nuts, and fatty fish, while avoiding saturated and trans fats.
3. Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates provide energy and help maintain blood sugar levels, which is especially important for those undergoing treatments that cause fatigue. Whole grains, fruits, and vegetables are excellent sources of complex carbohydrates that also provide fiber, which can help prevent constipation, a common side effect of treatment.
4. Vitamins and Minerals
Specific vitamins and minerals are crucial during cancer treatment, as they support the immune system and help the body recover from the side effects of cancer therapies. Some key vitamins and minerals include:
- Vitamin C: Important for immune function and tissue repair. Good sources include citrus fruits, strawberries, bell peppers, and broccoli.
- Vitamin D: Helps regulate the immune system and maintain strong bones. Vitamin D is found in fortified dairy products, fatty fish, and sunlight exposure.
- Zinc: Essential for immune function and wound healing. Zinc can be found in meat, shellfish, legumes, and seeds.
5. Antioxidants
Antioxidants are compounds that help neutralize free radicals in the body, which can damage cells and contribute to cancer progression. Fruits and vegetables, particularly those rich in colorful pigments, contain high levels of antioxidants. Examples include berries, leafy greens, and cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and kale.
6. Fiber
A high-fiber diet helps prevent constipation and supports overall digestive health. Fiber-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, are beneficial for gallbladder cancer patients, particularly those who may have digestive disturbances from treatment.
Foods to Include in the Diet
1. Lean Proteins
- Chicken breast
- Turkey
- Fish (salmon, tuna, mackerel)
- Tofu and tempeh
- Eggs and egg whites
- Beans and legumes
2. Fruits and Vegetables
- Dark leafy greens (spinach, kale, collard greens)
- Brightly colored vegetables (carrots, bell peppers, tomatoes)
- Berries (strawberries, blueberries, raspberries)
- Apples, oranges, bananas, and pears
3. Healthy Fats
- Olive oil
- Avocados
- Nuts and seeds (almonds, chia seeds, flaxseeds)
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines)
4. Whole Grains
- Oats
- Quinoa
- Brown rice
- Whole-wheat pasta
- Barley and bulgur
5. Hydration
Staying hydrated is essential, particularly during chemotherapy, when dehydration can exacerbate fatigue and nausea. Drinking plenty of water, herbal teas, and consuming hydrating foods such as cucumbers and watermelon can help maintain hydration.
Foods to Avoid
Certain foods can exacerbate treatment side effects or hinder the body’s ability to heal. These include:
- Processed Foods: Foods high in unhealthy fats, sugars, and sodium can cause inflammation and reduce overall health.
- Fried and Greasy Foods: These can be difficult to digest, especially after gallbladder removal or when the gallbladder is not functioning properly.
- Alcohol: Alcohol can interfere with the body’s ability to process nutrients and damage the liver, which is crucial for digestion and detoxification.
- Refined Carbohydrates: Foods such as white bread, sugary snacks, and sodas can spike blood sugar levels and lead to inflammation.
Nutrition plays a crucial role in the treatment and recovery process for individuals with gallbladder cancer. A balanced diet that supports the immune system, manages side effects, and aids in healing is essential for improving the overall quality of life during treatment. By focusing on protein, healthy fats, vitamins, minerals, and fiber, patients can help their bodies heal and improve their chances of recovery. While each individual’s dietary needs may vary, working with a nutritionist or healthcare provider is key to developing a personalized and effective nutrition plan.
With proper care, support, and attention to nutrition, individuals undergoing treatment for gallbladder cancer can experience better outcomes, reduce the severity of treatment side effects, and promote a faster and more effective recovery.