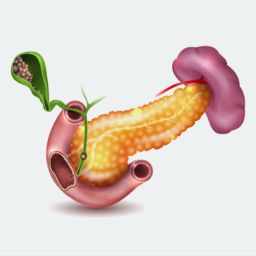
Risk Factors for Gallbladder Cancer
Several factors increase the risk of developing gallbladder cancer. Understanding these factors is key to reducing risk and preventing the disease.
- Gallstones: Gallstones are one of the most significant risk factors for gallbladder cancer. Chronic irritation of the gallbladder caused by gallstones can lead to the development of cancer.
- Chronic Inflammation: Conditions such as chronic cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder) and primary sclerosing cholangitis (a disease that causes inflammation and scarring of the bile ducts) are linked to an increased risk of gallbladder cancer.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can raise the risk of gallbladder cancer, as obesity is associated with higher levels of cholesterol and bile salts, which can increase the likelihood of gallstone formation.
- Age: The risk of gallbladder cancer increases with age. Most cases are diagnosed in individuals over 65.
- Gender: Gallbladder cancer is more common in women than in men, particularly those who have had multiple pregnancies or are obese.
- Family History: If you have a family member who has had gallbladder cancer or certain other cancers, your risk of developing the disease is higher.
- Exposure to Industrial Chemicals: Certain chemicals and toxins, particularly those used in the textile, rubber, and chemical industries, have been linked to a higher risk of gallbladder cancer.
- Other Health Conditions: Conditions such as diabetes, inflammatory bowel disease, and certain infections may increase the risk of gallbladder cancer.
Can Gallbladder Cancer Be Prevented?
While there is no surefire way to prevent gallbladder cancer, several lifestyle modifications and medical interventions can help reduce the risks associated with the disease. Many of the known risk factors for gallbladder cancer can be managed or mitigated by adopting healthier habits and seeking medical care for underlying conditions.
1. Healthy Diet and Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight and adopting a balanced diet are two of the most effective ways to reduce the risk of gallbladder cancer. Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of gallstones, which in turn raises the likelihood of gallbladder cancer. A diet high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, along with moderate portions of healthy fats, can help maintain a healthy weight and prevent obesity-related conditions that contribute to cancer risk.
Dietary Recommendations:
- Eat more fruits and vegetables: These foods are rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that support overall health and reduce the risk of cancer. Cruciferous vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts, in particular, have been shown to have cancer-fighting properties.
- Choose whole grains: Incorporate whole grains such as oats, quinoa, and brown rice into your diet instead of refined grains. Whole grains are high in fiber, which helps reduce the risk of gallstones and promotes digestive health.
- Limit unhealthy fats: While fats are necessary for the body, consuming excessive amounts of unhealthy fats, especially trans fats and saturated fats, can contribute to obesity and gallstone formation. Instead, choose healthy fats like olive oil, avocado, and fatty fish, which can help maintain gallbladder health.
- Increase fiber intake: A high-fiber diet helps prevent constipation, promotes healthy digestion, and may reduce the risk of developing gallstones.
2. Regular Physical Activity
Regular exercise is another key factor in preventing gallbladder cancer. Physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight and prevents obesity, which is a significant risk factor for gallbladder cancer. Exercise also helps regulate bile flow, which can reduce the likelihood of gallstone formation.
Recommendations:
- Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week, along with muscle-strengthening activities on two or more days each week.
- Activities such as walking, swimming, cycling, and yoga are great ways to stay active and improve overall health.
3. Preventing Gallstones
Since gallstones are a major risk factor for gallbladder cancer, reducing their formation is crucial in preventing the disease. While some individuals are genetically predisposed to developing gallstones, lifestyle changes can help lower the risk.
Tips to Prevent Gallstones:
- Avoid rapid weight loss: While losing weight is important, losing it too quickly can increase the risk of gallstone formation. Aim for a gradual weight loss of about 1-2 pounds per week.
- Maintain a healthy diet: As mentioned earlier, a diet high in fiber and low in unhealthy fats helps maintain a healthy gallbladder.
- Drink plenty of water: Staying hydrated helps maintain bile flow and reduces the risk of gallstones.
- Consider gallbladder removal in high-risk individuals: For people with a history of gallstones or other risk factors, doctors may recommend gallbladder removal (cholecystectomy) to prevent gallstone-related complications.
4. Managing Chronic Inflammation and Health Conditions
Conditions such as chronic cholecystitis, primary sclerosing cholangitis, and other inflammatory diseases of the gallbladder or bile ducts increase the risk of gallbladder cancer. Managing these conditions and seeking treatment for chronic inflammation can help reduce the risk.
- Monitor and treat gallbladder inflammation: If you have chronic gallbladder inflammation, work with your healthcare provider to manage the condition. In some cases, surgery to remove the gallbladder may be necessary.
- Control underlying health conditions: Conditions like diabetes and inflammatory bowel disease increase the risk of gallbladder cancer. Properly managing these diseases with medications, lifestyle changes, and regular medical check-ups can help mitigate this risk.
5. Avoiding Environmental Toxins
Exposure to certain chemicals and toxins, especially in industrial settings, has been linked to an increased risk of gallbladder cancer. If you work in an industry that involves exposure to harmful chemicals, take appropriate safety measures to limit your risk.
Recommendations:
- Follow safety protocols in workplaces where hazardous chemicals are used.
- Use protective equipment, such as gloves, masks, and ventilation systems, to reduce exposure to toxins.
- If possible, avoid unnecessary exposure to chemicals and pollutants.
6. Regular Health Screenings
While there are no routine screenings for gallbladder cancer for the general population, individuals at high risk due to family history or other factors may benefit from regular check-ups and diagnostic tests. Early detection increases the chances of successful treatment, so if you are at risk, discuss screening options with your doctor.
Tests for Early Detection:
- Ultrasound: Used to detect abnormalities in the gallbladder and surrounding organs.
- Blood tests: Including tests for tumor markers such as CA 19-9, which can indicate the presence of gallbladder cancer.
- Imaging tests: CT scans, MRIs, and endoscopic ultrasounds can help identify tumors or other issues in the gallbladder.
7. Genetic Counseling and Testing
If you have a family history of gallbladder cancer or related conditions, consider genetic counseling. Certain genetic mutations may increase the risk of gallbladder cancer, and knowing your genetic risk can guide preventive measures and early detection strategies.
While it is not possible to completely prevent gallbladder cancer, understanding its risk factors and adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the likelihood of its occurrence. Maintaining a healthy weight, following a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and managing chronic conditions are key strategies in lowering the risk of gallbladder cancer. For individuals at high risk, early detection through regular check-ups and screening can help catch the disease in its early stages, improving treatment outcomes.
By making these changes and taking proactive steps, individuals can lower their risk and live healthier lives, all while minimizing the impact of gallbladder cancer. If you are concerned about your risk for gallbladder cancer, consult with your healthcare provider to develop a plan for prevention and early detection tailored to your specific needs.