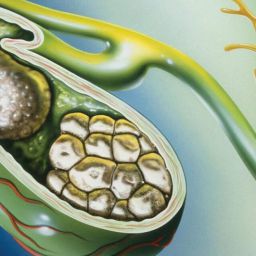
Prevalence of Gallstones
Gallstones are a global health concern, with a high prevalence in certain populations. It is estimated that about 10-15% of adults in Western countries have gallstones, although many people remain unaware of their condition because they experience no symptoms. Gallstones are more common in older adults, particularly in people over the age of 40. Additionally, women are at higher risk of developing gallstones compared to men, due to hormonal factors.
The prevalence of gallstones is also influenced by geographical location, with higher rates seen in North America and Europe. However, gallstones are becoming increasingly common in developing countries due to changes in diet and lifestyle.
Who Is at Higher Risk of Developing Gallstones?
Certain groups of people are more likely to develop gallstones based on a combination of genetics, lifestyle factors, and other health conditions. Understanding these risk factors can help individuals take preventive measures to reduce their chances of developing gallstones.
1. Gender
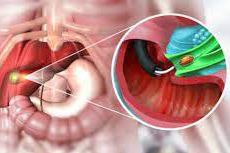
Women are more likely to develop gallstones than men, with studies showing that women are two to three times more likely to have gallstones. This increased risk is largely due to hormonal factors. The hormone estrogen, which is present at higher levels during pregnancy and in women taking birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy, can increase cholesterol levels in the bile, making gallstone formation more likely.
Additionally, during pregnancy, the gallbladder can become less effective at emptying, increasing the likelihood of gallstone formation. Pregnant women also experience changes in their hormonal balance, which further increases the risk of developing gallstones.
2. Age
Age is one of the strongest risk factors for gallstones. The risk of developing gallstones increases as people age, particularly after the age of 40. This is because the production of bile changes with age, leading to a higher concentration of cholesterol in the bile, which can contribute to the formation of cholesterol gallstones. In older adults, the gallbladder may also become less efficient in emptying, which can contribute to the development of gallstones.
3. Obesity and Overweight
One of the most significant risk factors for developing gallstones is being overweight or obese. Obesity leads to higher cholesterol levels in the bile, increasing the likelihood of cholesterol gallstone formation. Fatty tissue in the body can also interfere with bile secretion, leading to further complications.
Obesity, especially in individuals who have a body mass index (BMI) over 30, significantly increases the risk of gallstones. Additionally, rapid weight loss, such as that experienced through crash diets or bariatric surgery, can also increase the risk of gallstones. This is because quick weight loss causes the liver to release more cholesterol into the bile, which can contribute to the formation of stones.
4. Family History and Genetics

A family history of gallstones can increase an individual’s risk. Studies have shown that if a person’s close relatives (parents, siblings, or children) have had gallstones, the person is more likely to develop them as well. Genetics play a crucial role in this, as certain genetic factors may predispose individuals to high cholesterol levels or slow gallbladder emptying, both of which increase the likelihood of gallstone formation.
Individuals with a family history of gallbladder disease should be more vigilant about maintaining a healthy lifestyle to reduce the risk of developing gallstones.
5. Diet and Eating Habits
Diet plays a major role in the formation of gallstones. A high-fat, high-cholesterol diet, rich in refined carbohydrates and low in fiber, can increase the risk of developing gallstones. Diets that are rich in trans fats and refined sugars, commonly found in processed foods, are particularly harmful.
Conversely, a diet high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats (such as those found in olive oil, nuts, and fish) can help lower the risk of gallstones. Maintaining a balanced diet and avoiding excesses in fats and sugar can be a crucial preventive measure.
6. Diabetes
People with diabetes, particularly those with type 2 diabetes, are at higher risk of developing gallstones. This is because individuals with diabetes often have higher levels of cholesterol in their bile, which can contribute to the formation of cholesterol gallstones. Additionally, the use of certain medications, such as insulin, can further increase the risk.
Managing blood sugar levels through diet, exercise, and medication is important for people with diabetes to help reduce the risk of developing gallstones.
7. Pregnancy
Pregnant women are at a higher risk of developing gallstones due to hormonal changes. During pregnancy, estrogen and progesterone levels increase, which can lead to the production of more cholesterol in the bile. Additionally, the growing uterus can press on the gallbladder, making it less effective at emptying bile, increasing the likelihood of gallstone formation.
Pregnancy-related gallstones are more common in women who have had previous pregnancies or those who are older when pregnant. However, the risk generally decreases after childbirth.
8. Sedentary Lifestyle
A lack of physical activity and a sedentary lifestyle can contribute to the development of gallstones. Regular exercise helps maintain a healthy weight and promotes proper digestion, both of which are important in preventing gallstones. Physical inactivity can lead to weight gain, obesity, and high cholesterol levels, which are all risk factors for gallstone formation.
9. Certain Medical Conditions
Some medical conditions can increase the likelihood of developing gallstones. These include:
- Liver disease: Conditions such as cirrhosis and hepatitis can interfere with bile production and increase the risk of gallstones.
- Hyperlipidemia: High levels of cholesterol or triglycerides in the blood increase the risk of gallstones.
- Crohn’s disease: This inflammatory bowel disease can impair bile acid absorption and increase the risk of developing gallstones.
- Cystic fibrosis: This genetic condition can affect the pancreas and bile ducts, increasing the risk of gallstones.
10. Medications
Certain medications can also increase the risk of developing gallstones. These include medications that alter cholesterol levels, such as cholesterol-lowering drugs, as well as hormone therapies (such as birth control pills and hormone replacement therapy) and medications used to treat high blood pressure or diabetes.
Prevention and Management
While some risk factors for gallstones, such as age and family history, are beyond a person’s control, there are several lifestyle changes and preventive measures that can reduce the risk of developing gallstones:
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Gradual weight loss through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help reduce the risk of gallstones. Rapid weight loss should be avoided, as it increases the likelihood of gallstone formation.
- Eating a healthy diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats can reduce the risk of gallstones. Reducing the intake of processed foods, trans fats, and refined sugars is key.
- Regular physical activity: Engaging in regular exercise helps maintain a healthy weight and promotes proper digestion, both of which reduce the risk of gallstones.
- Managing underlying health conditions: People with diabetes, liver disease, or other medical conditions should work with their healthcare provider to manage these conditions and reduce their risk of developing gallstones.
- Avoiding certain medications: Individuals who are prescribed medications that increase the risk of gallstones should consult with their doctor about alternatives or preventive measures.
Gallstones are a common health issue that can affect anyone, but certain individuals are more at risk due to genetic, hormonal, and lifestyle factors. Women, older adults, those with obesity, and individuals with certain medical conditions are particularly vulnerable to developing gallstones. Understanding these risk factors and making lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight and eating a balanced diet, can help reduce the risk of gallstones. Regular check-ups and early detection are also important to prevent complications associated with gallstones, ensuring overall digestive health and well-being.