1. Hemorrhoids: A Common Cause of Rectal Bleeding
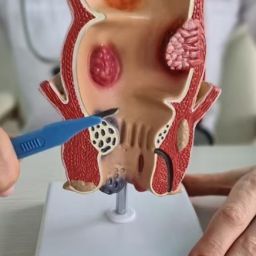
Hemorrhoids are one of the most frequent causes of rectal bleeding. They are swollen or inflamed blood vessels in the rectum or anus, which can cause discomfort, itching, and, in some cases, bleeding. Hemorrhoids can occur due to several factors, including prolonged sitting, straining during bowel movements, pregnancy, obesity, and a low-fiber diet.
1.1 Symptoms of Hemorrhoids
The symptoms of hemorrhoids can vary depending on the severity of the condition. The most common symptoms include:
- Bright Red Blood: One of the primary signs of hemorrhoids is bright red blood on the toilet paper or in the toilet bowl after a bowel movement. This blood is typically fresh and appears on the surface of the stool.
- Itching or Irritation: Hemorrhoids often cause itching, irritation, or discomfort around the anus due to the swelling and inflammation of the blood vessels.
- Pain or Discomfort: In some cases, hemorrhoids can cause pain, particularly during bowel movements. This is more common with external hemorrhoids, which are located around the anal opening.
- Lumps or Swelling: External hemorrhoids can be felt as small lumps around the anus, which may be tender or sensitive to touch.
1.2 Risk Factors for Hemorrhoids
Certain lifestyle factors increase the likelihood of developing hemorrhoids. These include:
- Chronic Constipation or Diarrhea: Straining during bowel movements due to constipation or frequent loose stools can contribute to the formation of hemorrhoids.
- Pregnancy: The increased pressure on the pelvic region during pregnancy can cause hemorrhoids, and they are common in women during and after childbirth.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts pressure on the abdominal area, which can contribute to hemorrhoids.
- Prolonged Sitting: Sitting for extended periods, especially on the toilet, can put pressure on the rectal area, leading to hemorrhoid development.
- Low-Fiber Diet: A diet low in fiber can lead to constipation, which increases the risk of hemorrhoids.
While hemorrhoids are typically not serious, they can lead to significant discomfort and quality-of-life issues. However, it is essential to recognize that rectal bleeding can also be caused by more serious conditions.
2. When Rectal Bleeding Could Indicate a More Serious Condition
Although hemorrhoids are a common cause of rectal bleeding, there are several other conditions that can cause bleeding from the rectum, some of which may be more serious. It is crucial to understand when rectal bleeding may signal a need for further investigation and potential treatment for a more severe issue.
2.1 Colorectal Cancer
Colorectal cancer is one of the most concerning causes of rectal bleeding. It occurs when abnormal cells grow in the colon or rectum and form tumors that can bleed. While colorectal cancer can be asymptomatic in its early stages, rectal bleeding is often one of the first noticeable signs.
Symptoms of Colorectal Cancer
- Blood in Stool: Colorectal cancer can cause intermittent bleeding, which may be present as dark or tarry stool, indicating that the blood has been digested. Alternatively, fresh red blood may appear on the toilet paper.
- Change in Bowel Habits: Individuals with colorectal cancer may experience changes in their bowel habits, such as diarrhea, constipation, or a feeling of incomplete evacuation.
- Abdominal Pain: Unexplained pain or cramping in the abdomen can be a symptom of colorectal cancer, particularly as the tumor obstructs the bowel.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Unexplained weight loss, fatigue, and a general feeling of weakness may accompany colorectal cancer.
Risk Factors for Colorectal Cancer
- Age: Individuals over the age of 50 are at a higher risk of colorectal cancer, although it can affect younger individuals as well.
- Family History: A family history of colorectal cancer or certain inherited genetic conditions can increase the likelihood of developing the disease.
- Lifestyle Factors: A diet high in red or processed meats, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption can increase the risk of colorectal cancer.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Conditions such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis increase the risk of colorectal cancer.
2.2 Anal Cancer
Anal cancer is another potential cause of rectal bleeding. It is a relatively rare form of cancer that affects the anus and is typically linked to infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV). Like colorectal cancer, anal cancer can cause bleeding, discomfort, and changes in bowel habits.
Symptoms of Anal Cancer
- Pain or Bleeding: Pain or bleeding around the anus is a common symptom of anal cancer.
- Lumps or Masses: A lump or mass near the anus may be felt during a physical examination.
- Changes in Bowel Movements: Anal cancer may cause a change in bowel movements, such as a feeling of incomplete evacuation or the passage of narrower stools.
- Itching or Discharge: Individuals with anal cancer may experience persistent itching or unusual discharge from the anus.
2.3 Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
Inflammatory bowel disease, including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, is a group of chronic conditions that cause inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. These conditions can lead to rectal bleeding due to the damage caused to the lining of the intestines.
Symptoms of IBD
- Blood in Stool: Rectal bleeding is common in individuals with IBD, particularly in cases of ulcerative colitis.
- Diarrhea: Chronic diarrhea, often accompanied by blood or mucus, is a hallmark symptom of IBD.
- Abdominal Cramping: Abdominal pain or cramping, especially after eating, is a common complaint in individuals with IBD.
- Fatigue and Weight Loss: Individuals with IBD may experience unexplained weight loss and fatigue due to the chronic nature of the condition.
2.4 Other Potential Causes of Rectal Bleeding
In addition to the conditions listed above, several other factors can contribute to rectal bleeding, including:
- Anal Fissures: Small tears in the skin around the anus can lead to bleeding, especially during or after a bowel movement.
- Diverticular Disease: Diverticula (small pouches) that form in the colon can become inflamed or infected, leading to bleeding.
- Proctitis: Inflammation of the rectum, often caused by infections or radiation therapy, can lead to bleeding and discomfort.
3. When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience rectal bleeding, it is essential to determine the underlying cause. In many cases, rectal bleeding may be attributed to benign conditions like hemorrhoids or anal fissures. However, bleeding can also indicate a more serious condition, and timely medical evaluation is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
When to Seek Help:
- Persistent Bleeding: If bleeding continues over a prolonged period or worsens, it is essential to seek medical attention.
- Change in Bowel Habits: If you experience a sudden change in bowel habits, such as ongoing diarrhea, constipation, or narrow stools, a healthcare professional should be consulted.
- Unexplained Weight Loss or Fatigue: If you experience unexplained weight loss or persistent fatigue alongside rectal bleeding, it could be indicative of a more serious condition.
- Severe Pain: Severe abdominal or rectal pain that does not subside may be a sign of an underlying issue that requires medical attention.
4. Diagnosis of Rectal Bleeding
To diagnose the cause of rectal bleeding, a healthcare provider will conduct a thorough examination and may recommend additional tests, such as:
- Physical Exam: A visual examination of the anus and rectum can help identify hemorrhoids, anal fissures, or signs of other conditions.
- Endoscopy: Procedures like a colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy may be recommended to examine the colon and rectum for any abnormalities.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests may be used to check for anemia (which can result from chronic blood loss) or signs of infection.
- Imaging: In some cases, imaging tests such as a CT scan or MRI may be used to further investigate the source of the bleeding.
5. Treatment of Rectal Bleeding
The treatment of rectal bleeding depends on its underlying cause. For hemorrhoids, treatments may include lifestyle changes, topical medications, or, in severe cases, surgical interventions. For more serious conditions such as colorectal cancer or IBD, treatment may involve surgery, chemotherapy, or immunotherapy.
Rectal bleeding is a symptom that can be caused by a variety of conditions, ranging from relatively benign issues like hemorrhoids to more serious concerns such as colorectal cancer or inflammatory bowel disease. Understanding the potential causes of rectal bleeding and seeking timely medical evaluation is essential for ensuring the best possible outcomes. If you experience any form of rectal bleeding, it is important not to ignore the symptom and to consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.