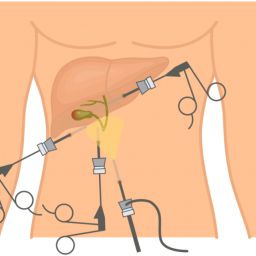
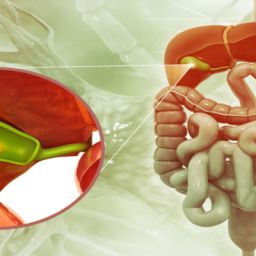
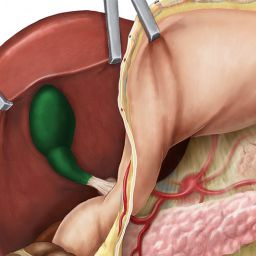
Gallstones and Their Effects on Health
Gallstones are hardened deposits that form in the gallbladder, often due to an imbalance in the substances that make up bile, a digestive fluid produced by the liver. There are two main types of gallstones:
- Cholesterol Gallstones: These are the most common type and form when there is too much cholesterol in the bile, leading to the formation of hard crystals.
- Pigment Gallstones: These are smaller and darker, made from bilirubin, a byproduct of red blood cell breakdown. Pigment gallstones are often associated with certain medical conditions like liver disease or infections in the bile ducts.
When gallstones obstruct bile flow, they can cause intense pain, bloating, and digestive problems. This is known as a “gallstone attack,” which can be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, fever, or even jaundice. In some cases, gallstones may lead to more severe complications, such as inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis) or inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis).
Although treatment options vary, a significant part of managing gallstones involves modifying one’s daily habits, particularly in the areas of diet, physical activity, and stress management.
1. Dietary Considerations for Gallstone Management
One of the most effective ways to manage gallstones and prevent further complications is through dietary changes. What you eat and how often you eat can have a significant impact on the functioning of your gallbladder.

a. Adopt a Low-Fat Diet
A high-fat diet can exacerbate gallstone symptoms and contribute to the formation of new stones. Fatty foods stimulate the gallbladder to release bile, which can cause pain if gallstones are present. Therefore, individuals with gallstones should limit their intake of saturated fats and opt for healthier fat sources.
Foods to avoid:
- Fried foods: These are high in unhealthy fats and can trigger gallbladder attacks.
- Fatty meats: Red meat, bacon, and processed meats contain high amounts of saturated fat, which should be minimized.
- Full-fat dairy products: Whole milk, butter, cheese, and cream are all high in fat.
Healthy fat alternatives:
- Olive oil: A great source of monounsaturated fats that are easier for the body to process.
- Nuts and seeds: Almonds, walnuts, and flaxseeds provide healthy fats and fiber.
- Avocados: Rich in heart-healthy fats and fiber, avocados are an excellent addition to a gallstone-friendly diet.
- Fatty fish: Salmon, mackerel, and sardines contain omega-3 fatty acids that are beneficial for heart and digestive health.
b. Focus on High-Fiber Foods
Fiber helps regulate digestion and can improve gallbladder function by reducing the concentration of cholesterol in bile. High-fiber foods also help prevent constipation, which is important for overall digestive health.
Fiber-rich foods to include:
- Whole grains: Brown rice, quinoa, whole wheat bread, and oats are excellent sources of fiber.
- Fruits and vegetables: Apples, berries, carrots, broccoli, and spinach provide plenty of fiber and essential nutrients.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, chickpeas, and peas are rich in fiber and plant-based protein.
c. Maintain Regular Meal Timing
For individuals with gallstones, eating smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day is recommended. Large meals can overwhelm the digestive system, putting additional strain on the gallbladder and increasing the likelihood of a gallstone attack.
Meal timing recommendations:
- Aim for 4-6 small meals per day instead of 2-3 large meals.
- Include a balance of protein, healthy fats, and fiber in each meal to maintain stable blood sugar levels and prevent gallbladder stress.
- Avoid eating large meals late at night to prevent digestive discomfort.
2. Regular Physical Activity
Physical activity plays a crucial role in managing gallstones and maintaining overall health. Exercise can help prevent obesity, which is a significant risk factor for gallstone formation, and it may also help manage cholesterol levels and improve bile flow.
a. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Obesity is one of the leading risk factors for developing gallstones, particularly cholesterol gallstones. Losing weight gradually and maintaining a healthy weight can help prevent the formation of new stones and reduce the risk of complications. However, rapid weight loss can increase the risk of gallstone formation, as the liver releases excess cholesterol into the bile during fast weight loss.
Weight loss guidelines:
- Aim for gradual weight loss, around 1-2 pounds (0.5-1 kg) per week.
- Combine exercise with a balanced diet that emphasizes whole foods and healthy fats.
b. Incorporate Cardio and Strength Training
Regular exercise, including both cardiovascular activities and strength training, is beneficial for improving overall health and managing gallstones. Cardio exercises, such as walking, cycling, swimming, and jogging, can help improve circulation and support weight loss.
Strength training exercises, such as bodyweight exercises, resistance bands, or weightlifting, help build muscle mass and boost metabolism.
c. Avoid Sedentary Behavior
Sitting for prolonged periods can contribute to weight gain, poor circulation, and sluggish digestion. Aim to stay active throughout the day, even if it’s just taking short walks or stretching every hour.
3. Stress Management
Chronic stress can have a negative impact on digestive health, including the functioning of the gallbladder. Stress can exacerbate digestive issues, slow down the body’s ability to process fats, and even trigger gallbladder attacks.
a. Practice Relaxation Techniques
To manage stress, individuals with gallstones should engage in relaxation techniques, such as:
- Deep breathing exercises: These can help calm the nervous system and reduce stress.
- Yoga and meditation: These practices promote relaxation, flexibility, and mindfulness, which can have positive effects on overall health.
- Progressive muscle relaxation: This involves systematically tensing and relaxing muscle groups to reduce tension and stress.
b. Prioritize Sleep
Getting adequate sleep is crucial for stress management and overall health. Sleep allows the body to repair itself, regulate hormones, and support immune function. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night, and create a relaxing bedtime routine to ensure restful sleep.
4. Hydration and Fluid Intake
Adequate hydration is essential for individuals with gallstones. Dehydration can lead to concentrated bile, which increases the likelihood of gallstone formation. It’s important to drink plenty of water throughout the day to keep bile flowing and prevent complications.
a. Drink Plenty of Water
Aim to drink at least 8 cups (2 liters) of water per day, or more if you are physically active or live in a hot climate. Water helps dilute bile and promotes healthy digestion.
b. Limit Caffeine and Alcohol
While moderate caffeine intake is generally safe, excessive consumption can irritate the digestive system. Similarly, alcohol can increase the risk of developing gallstones and should be consumed in moderation or avoided altogether.
5. Regular Medical Check-Ups and Monitoring
Gallstones can often go unnoticed, especially in the early stages. Therefore, it’s essential for individuals with gallstones or at risk of developing them to schedule regular medical check-ups. Early detection of symptoms or complications can lead to more effective treatment and prevent the need for more invasive procedures.
a. Monitor Symptoms
If you experience symptoms such as severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, fever, or jaundice, it’s important to seek medical attention immediately. These symptoms may indicate that a gallstone is blocking a bile duct or that an infection has developed.
b. Work with Your Doctor
Consult with your healthcare provider to create a comprehensive plan for managing gallstones. This may include dietary recommendations, lifestyle changes, and, if necessary, medications or surgical options, such as gallbladder removal.
6. Alternative Therapies and Supplements
Some individuals with gallstones may benefit from alternative therapies and supplements to support their digestive health. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before incorporating any new treatments.
a. Herbal Remedies
Certain herbs, such as milk thistle, dandelion, and turmeric, are believed to support liver and gallbladder health. These herbs may promote bile production, reduce inflammation, and aid in digestion. Always consult with a healthcare provider before using herbal supplements, especially if you are taking other medications.
b. Probiotics
Probiotics, found in fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, and kimchi, help support healthy gut bacteria. A healthy gut microbiome can contribute to better digestion and may help prevent constipation, a common issue for those with gallstones.
Living with gallstones requires careful attention to various aspects of daily life, from diet and exercise to stress management and medical care. By making thoughtful lifestyle changes, individuals with gallstones can reduce the risk of complications, manage symptoms, and improve their overall quality of life.
Incorporating a low-fat, high-fiber diet, maintaining regular physical activity, practicing stress management techniques, and staying hydrated can go a long way in supporting gallbladder health. Regular medical check-ups and monitoring symptoms are equally important for early detection and treatment.
By following these guidelines, individuals with gallstones can successfully manage their condition and enjoy a healthy, active life. Always consult with a healthcare provider before making significant changes to your lifestyle, particularly if you are experiencing symptoms or have underlying health conditions.