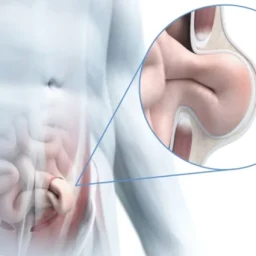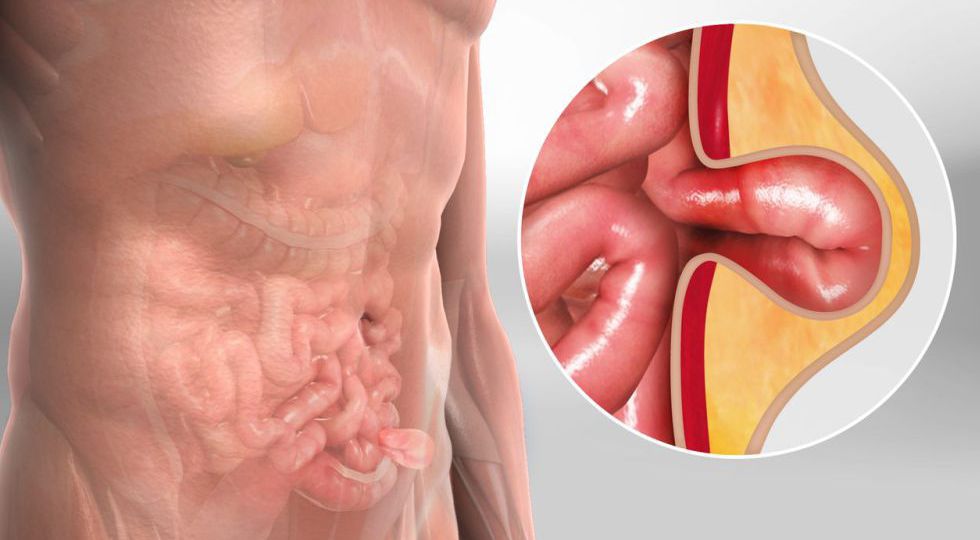
1. What Is an Inguinal Hernia and How Is It Treated?
To understand the risk of recurrence, it’s essential to first define what an inguinal hernia is and how it is treated.
- Inguinal Hernia: An inguinal hernia occurs when a part of the intestine or abdominal tissue pushes through a weak spot or opening in the abdominal wall, usually in the groin area. This can cause a visible bulge, discomfort, and in some cases, severe pain.
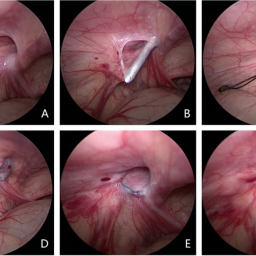
- Surgical Treatment: The primary method for treating an inguinal hernia is surgery, which can be performed using open or laparoscopic techniques. The goal of surgery is to push the herniated tissue back into place and reinforce the abdominal wall to prevent future protrusions. In most cases, a synthetic mesh is used to strengthen the weakened area, which reduces the risk of recurrence.
2. What Factors Influence the Risk of Recurrence?
The likelihood of a recurrence after inguinal hernia surgery is influenced by several factors, ranging from the patient’s health and lifestyle to the surgical technique used. Understanding these factors is essential for reducing the risk of the hernia returning.
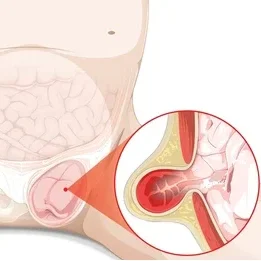
- Surgical Technique: The type of surgery performed plays a significant role in the risk of recurrence. Laparoscopic surgery, for example, has been shown to have lower recurrence rates compared to traditional open surgery due to its minimally invasive nature and better visualization of the hernia site.
- Use of Mesh: Mesh repair is the gold standard for inguinal hernia surgery because it provides additional support to the abdominal wall, significantly reducing the chances of the hernia recurring. Failure to use mesh, or using inferior quality mesh, can lead to higher recurrence rates.
- Surgeon Experience: The skill and experience of the surgeon can have a significant impact on the outcome of the surgery. Surgeons with extensive experience in hernia repair tend to have lower recurrence rates because they are more adept at handling complications during the procedure and ensuring a more durable repair.
- Patient’s Age and Health: Older adults may experience slower healing times, and those with chronic health conditions such as obesity, diabetes, or respiratory issues may be at higher risk for complications and recurrence. Additionally, those with weakened immune systems may struggle to heal properly after surgery, leading to a higher risk of hernia recurrence.
- Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, poor nutrition, and lack of physical activity can all interfere with healing and increase the likelihood of recurrence. Smoking, in particular, has been linked to an increased risk of complications such as wound infections and impaired tissue healing, which can contribute to hernia recurrence.
3. How Common Is Hernia Recurrence After Surgery?
Hernia recurrence rates vary based on the type of surgery, the surgeon’s experience, and the patient’s overall health. Studies suggest that recurrence rates after inguinal hernia surgery can range from 1% to 10%, depending on these variables.
- Open Surgery: In open hernia repair, the recurrence rate is generally higher, particularly if mesh is not used or if there is a failure to properly close the abdominal wall. Recurrence rates for open surgeries can range from 2% to 10%.
- Laparoscopic Surgery: Recurrence rates are lower for laparoscopic surgery, with some studies suggesting rates as low as 1% to 5%. The minimally invasive nature of laparoscopic surgery allows for better precision and smaller incisions, which contribute to a reduced likelihood of recurrence.
- Factors that Increase Risk: Older age, obesity, infection, smoking, and other underlying health issues all increase the likelihood of a hernia recurring after surgery. Understanding these risks can help patients take preventative measures and improve their overall recovery.
4. Why Do Hernias Recur After Surgery?
The recurrence of an inguinal hernia after surgery is caused by several factors, including complications during the procedure and issues related to the patient’s recovery.
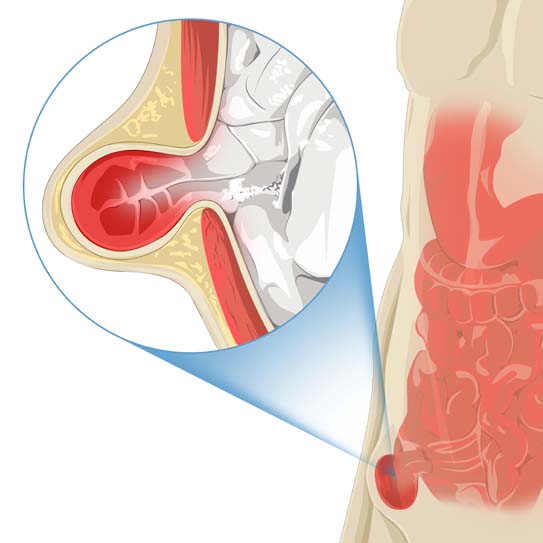
- Surgical Complications: If the surgical repair is not performed correctly, or if the mesh used is not properly secured, the risk of recurrence increases. In some cases, a complication such as wound infection, hematoma, or seroma can weaken the surgical site and make the hernia more likely to recur.
- Inadequate Healing: If the abdominal wall does not heal properly after surgery, the risk of the hernia returning is higher. This can happen if the patient experiences issues like infection, poor circulation, or excessive tension on the repair site.
- Obesity and Lifestyle Factors: Excess weight can place additional pressure on the abdominal wall, making it more likely that the hernia will reappear. Patients who fail to make the necessary lifestyle changes, such as improving diet and exercise habits, may be at higher risk for recurrence.
- Premature Physical Activity: Engaging in strenuous physical activity too soon after surgery can cause undue pressure on the repair site, leading to complications and an increased risk of recurrence. It is important to follow post-operative instructions regarding activity levels and weightlifting restrictions.
5. How Can the Risk of Hernia Recurrence Be Minimized?
There are several strategies that patients can adopt to minimize the risk of recurrence after inguinal hernia surgery. By following these preventative measures, patients can improve their chances of a successful, long-term recovery.
- Choosing the Right Surgeon: Selecting a highly experienced surgeon who is well-versed in hernia repair can help ensure that the procedure is performed correctly and that the risk of recurrence is minimized. Surgeons who specialize in laparoscopic techniques tend to have lower recurrence rates.
- Use of High-Quality Mesh: The use of a durable, high-quality mesh is essential for preventing recurrence. Mesh helps reinforce the abdominal wall, providing long-term support and reducing the risk of a hernia returning.
- Post-Surgical Care: Proper post-surgical care is vital for a smooth recovery. Patients should follow their surgeon’s instructions carefully, avoid lifting heavy objects or engaging in strenuous activity too soon, and attend follow-up appointments to monitor healing.
- Managing Weight: Maintaining a healthy weight is one of the most effective ways to reduce the risk of hernia recurrence. Obesity increases abdominal pressure, which can stress the surgical repair site and lead to complications.
- Avoiding Smoking: Smoking impairs the body’s ability to heal and can contribute to complications like wound infections, which increase the risk of recurrence. Quitting smoking before and after surgery can significantly improve recovery outcomes.
- Diet and Nutrition: Eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals helps promote tissue healing and strengthens the body’s immune system. A healthy diet also supports weight management, reducing pressure on the abdominal wall.
- Physical Therapy: Some patients may benefit from physical therapy post-surgery to help strengthen the abdominal muscles and prevent further strain on the surgical site. A physical therapist can guide patients through appropriate exercises and stretches to aid in recovery.
6. When Should You Consider Revision Surgery?
In some cases, despite following all preventative measures, a hernia may recur. If this happens, patients may need to consider revision surgery to repair the hernia once again. Revision surgery is more complex than the initial procedure and may involve a more extensive approach, depending on the severity of the recurrence and the location of the hernia.
- Signs of Recurrence: Symptoms of recurrence can include the reappearance of a bulge in the groin area, pain or discomfort during physical activity, and swelling. If any of these symptoms are noticed, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider promptly.
- Deciding on Revision Surgery: If recurrence is confirmed, revision surgery may be necessary. The surgeon will evaluate the severity of the recurrence and recommend the best course of action, which may include repairing the hernia using different techniques, additional mesh, or other strategies to improve long-term outcomes.
While inguinal hernia surgery is generally effective, recurrence remains a possibility. Understanding the risk factors for recurrence and taking proactive steps to manage the condition can significantly improve outcomes for patients. Choosing an experienced surgeon, using high-quality mesh, managing lifestyle factors, and following post-surgical care instructions are essential to reducing the risk of recurrence.
Though recurrence is relatively uncommon, it is important to remain vigilant and consult with a healthcare provider if symptoms reappear. With proper care, most individuals can recover fully and enjoy a hernia-free life.