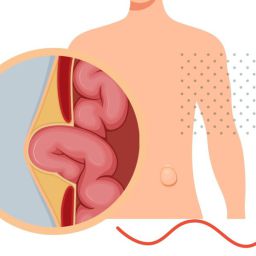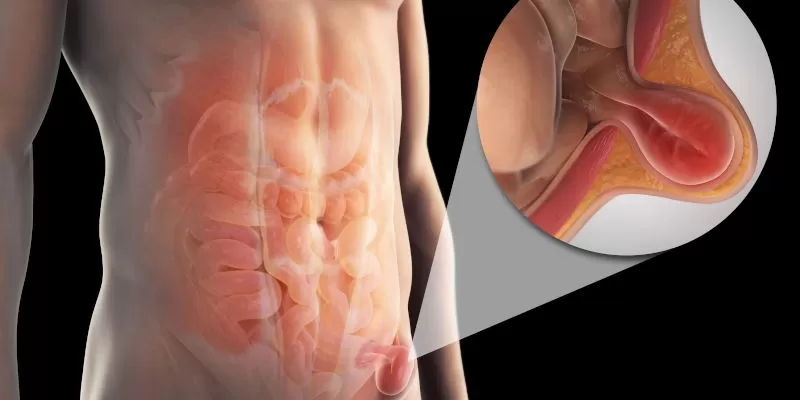
Traditional Treatment for Inguinal Hernia
The standard treatment for inguinal hernia is surgical repair, which is typically recommended when the hernia causes pain, is growing in size, or is at risk of complications like strangulation (when the blood supply to the herniated tissue is cut off). There are two main types of surgery:
- Open Surgery: This involves making a large incision in the groin area to push the herniated tissue back into place and strengthen the abdominal wall with a mesh.
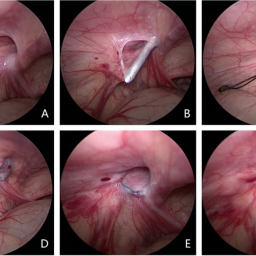
- Laparoscopic Surgery: This minimally invasive technique uses small incisions and a camera to guide the surgeon in repairing the hernia, offering shorter recovery times and less pain.
While surgery is often considered the most effective treatment for inguinal hernia, some individuals may seek alternative treatments, particularly when the hernia is small, asymptomatic, or if they wish to avoid surgery due to medical or personal reasons.
The Role of Alternative Methods in the Treatment of Inguinal Hernia
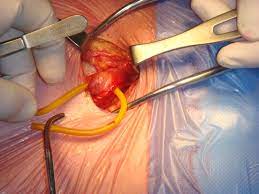
Although surgery remains the gold standard in hernia treatment, many patients explore alternative methods either as complementary treatments or as a way to manage the condition without immediate surgery. While these methods may not directly repair the hernia, they can help alleviate symptoms, prevent the hernia from worsening, and improve overall health and well-being. Let’s examine the various alternative methods that have been used in the management of inguinal hernia.
1. Herbal Remedies
Herbal medicine is one of the most commonly used alternative treatments for managing inguinal hernia symptoms. Some herbs are believed to strengthen the abdominal muscles, reduce inflammation, and improve circulation, which may help support the hernia area. However, it’s essential to understand that herbal remedies should only be used in conjunction with professional medical advice and not as a substitute for surgery if the hernia is severe.
- Turmeric: Known for its anti-inflammatory properties, turmeric may help reduce inflammation around the hernia and provide some relief from pain. Curcumin, the active compound in turmeric, has also been shown to have antioxidant and healing properties.
- Ginger: Ginger has anti-inflammatory and digestive properties, which may help alleviate discomfort caused by an inguinal hernia, especially when bloating or digestive issues accompany the condition.
- Chamomile: Chamomile is often used to reduce muscle spasms and inflammation. It may provide relief if the hernia is causing muscle tension in the groin area.
- Witch Hazel: Used externally as a compress, witch hazel is believed to reduce swelling and provide soothing relief for inflamed areas of the body, including the groin.
2. Physical Therapy and Core Strengthening Exercises
Physical therapy plays a significant role in the conservative management of inguinal hernia, particularly for individuals who want to avoid surgery or who are in the early stages of the condition. Strengthening the muscles of the abdominal wall and core can help provide support to the hernia and alleviate symptoms. Targeted exercises may improve muscle tone and reduce the pressure on the weak spot in the abdominal wall.
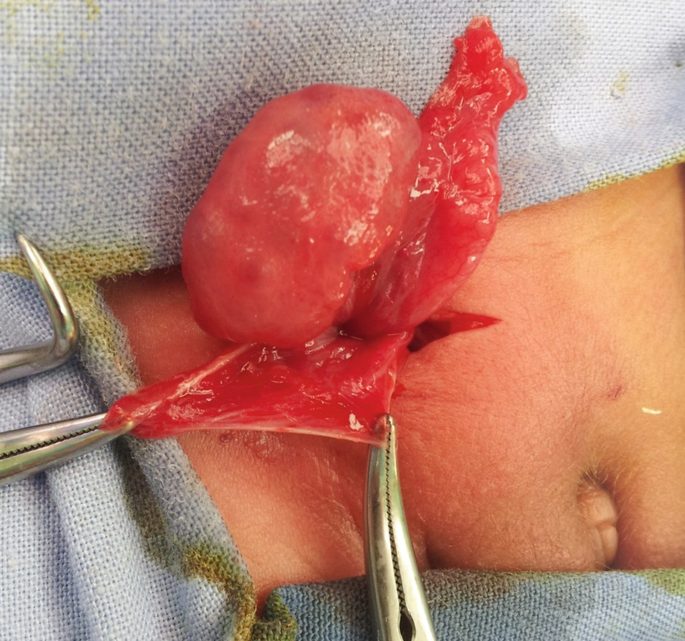
- Core Strengthening: Exercises that target the core muscles, including the abdominal and pelvic muscles, can help stabilize the area around the hernia. These exercises may include abdominal crunches, leg raises, and gentle pelvic tilts. A physical therapist can guide patients in performing these exercises safely.
- Pelvic Floor Exercises: Strengthening the pelvic floor muscles can help improve overall abdominal stability and prevent the hernia from worsening.
- Postural Exercises: Improving posture through stretching and strengthening can reduce strain on the abdominal muscles and help prevent the hernia from becoming more pronounced.
While these exercises may provide relief and reduce discomfort, they should be performed under the guidance of a medical professional to ensure they do not exacerbate the condition.
3. Acupuncture
Acupuncture, an ancient practice from Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body to stimulate energy flow, promote healing, and reduce pain. In the context of inguinal hernia, acupuncture may help relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and improve blood circulation to the affected area.
While acupuncture has shown promise for pain management in various conditions, scientific evidence supporting its efficacy in treating inguinal hernia is limited. However, it may be helpful as part of a holistic approach to managing symptoms and improving overall well-being.
4. Massage Therapy
Massage therapy is another alternative treatment that may be used to relieve the symptoms of inguinal hernia. Gentle massage techniques applied to the lower abdomen and groin area can help improve circulation, reduce muscle tension, and promote relaxation.
While massage therapy cannot repair the hernia itself, it may provide temporary relief from discomfort and help alleviate muscle spasms or tension that can arise around the hernia site. It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider before using massage therapy, particularly if the hernia is large or causing significant pain.
5. Diet and Lifestyle Modifications
Diet and lifestyle changes play a crucial role in managing inguinal hernia, particularly when it comes to reducing symptoms and preventing the condition from worsening. Excess abdominal pressure, caused by obesity, constipation, or poor dietary habits, can exacerbate the hernia.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the pressure on the abdominal wall, decreasing the likelihood of the hernia worsening. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support overall health and weight management.
- High-Fiber Diet: Constipation can worsen hernia symptoms by causing straining during bowel movements. A high-fiber diet can help prevent constipation and reduce the need for straining.
- Avoiding Heavy Lifting: Lifting heavy objects increases intra-abdominal pressure, which can aggravate an inguinal hernia. Adopting proper lifting techniques and avoiding heavy lifting can help manage symptoms and prevent complications.
The Effectiveness and Limitations of Alternative Methods
While alternative methods may provide relief from symptoms and improve overall quality of life, it is important to understand that these treatments do not address the root cause of the hernia itself. Inguinal hernias, especially larger or more complicated ones, typically require surgical intervention to prevent complications such as strangulation or bowel obstruction.
Alternative methods should be used in conjunction with conventional medical care and under the guidance of healthcare professionals. They are most effective for managing mild cases, alleviating symptoms, or improving overall health, but they should not replace surgery when it is necessary.
The role of alternative methods in the treatment of inguinal hernia is primarily focused on symptom management and improving overall well-being. While these methods, such as herbal remedies, physical therapy, acupuncture, and lifestyle modifications, may offer temporary relief and help prevent the condition from worsening, surgery remains the most effective and reliable treatment for most patients. Individuals considering alternative treatments should consult with their healthcare providers to ensure a comprehensive approach to managing their hernia and to discuss whether surgery is ultimately necessary.
By combining conventional and alternative treatments, patients can take a proactive approach to managing their inguinal hernia and enhance their quality of life.