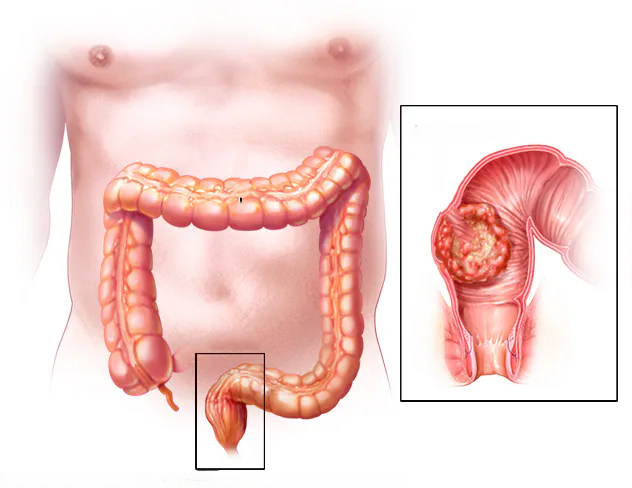
1. Importance of a Balanced Diet for Rectal Health
1.1 Role of Fiber in Preventing Rectal Disorders
Fiber plays a crucial role in maintaining rectal health by promoting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation. Constipation can strain the rectum, leading to conditions like hemorrhoids, anal fissures, and rectal prolapse.
- Insoluble Fiber: Found in foods such as whole grains, vegetables, and nuts, insoluble fiber helps add bulk to the stool, making it easier to pass.
- Soluble Fiber: Found in foods like oats, fruits, and legumes, soluble fiber absorbs water, softening the stool and making it more comfortable to eliminate.
1.2 Recommended Fiber Intake
It is recommended that adults consume between 25 to 30 grams of fiber per day. A fiber-rich diet not only promotes rectal health but also reduces the risk of colorectal cancer by maintaining regular bowel movements and improving gut microbiota.
1.3 Other Key Nutrients for Rectal Health
While fiber is essential, other nutrients also support rectal health:
- Water: Staying hydrated is vital for softening stool and facilitating easy bowel movements.
- Healthy Fats: Incorporating healthy fats from sources like avocados, olive oil, and fatty fish can help lubricate the digestive system and prevent constipation.
- Antioxidants: Foods rich in antioxidants, such as berries, leafy greens, and tomatoes, help protect the rectal tissues from oxidative damage and promote healing.
1.4 Foods to Avoid for Rectal Health
Certain foods can contribute to rectal discomfort or worsen existing conditions:
- Processed Foods: High in unhealthy fats, sugars, and salt, processed foods can increase inflammation and slow down digestion.
- Red Meat: Excessive consumption of red meat has been linked to an increased risk of colorectal cancer.
- Spicy Foods: For individuals with sensitive digestive systems, spicy foods may irritate the rectum and lead to flare-ups of conditions like hemorrhoids or anal fissures.
2. Maintaining Proper Hydration
2.1 How Water Supports Rectal Health
Proper hydration is essential for preventing constipation, which can lead to rectal strain. Water helps soften stool, making it easier to pass without excessive straining. Dehydration, on the other hand, can lead to hard, dry stools, contributing to the development of hemorrhoids or anal fissures.
2.2 Recommended Daily Water Intake
For most people, the general guideline is to drink at least eight 8-ounce glasses of water per day (about 2 liters). However, individuals who consume more fiber or engage in vigorous physical activity may need more fluids to support digestion.
2.3 Hydrating Foods for Rectal Health
In addition to water, certain foods can help improve hydration levels and promote healthy bowel movements:
- Watermelon, cucumber, and celery are all rich in water content.
- Soups and broths are another great way to maintain hydration.
3. Physical Activity and Its Role in Rectal Health
3.1 The Impact of Exercise on Digestion
Regular physical activity has numerous benefits for gastrointestinal health, including improving digestion, preventing constipation, and maintaining a healthy weight. Exercise helps stimulate the muscles of the digestive system, promoting regular bowel movements and reducing the risk of rectal disorders.
3.2 Recommended Exercises for Rectal Health
Engaging in aerobic activities such as walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling can help improve gut motility and prevent constipation. Strength training exercises also benefit the pelvic floor muscles, which support the rectum and anus.
3.3 The Importance of Kegel Exercises for Rectal and Pelvic Health
Kegel exercises, which involve contracting and relaxing the pelvic floor muscles, are particularly important for individuals with rectal conditions like incontinence or prolapse. Strengthening the pelvic floor can improve bowel control, reduce pressure on the rectum, and enhance overall rectal health.
4. Hygiene Practices for Maintaining Rectal Health
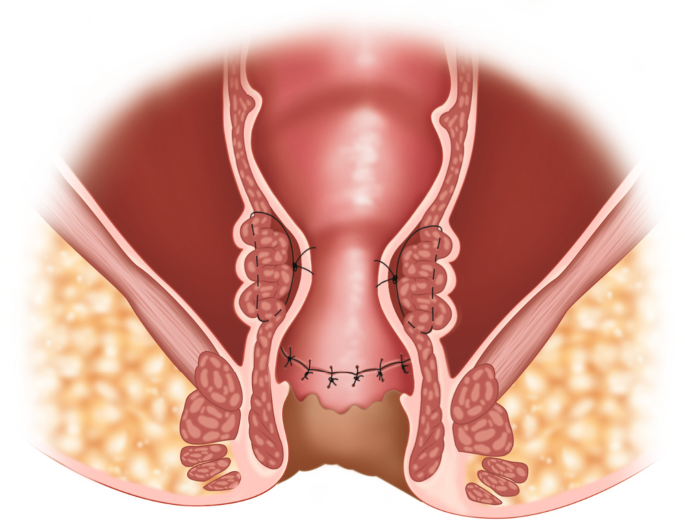
4.1 The Role of Proper Hygiene in Preventing Rectal Disorders
Maintaining proper hygiene in the anal area is essential for preventing infections, irritation, and conditions like hemorrhoids. Poor hygiene can lead to bacterial growth, skin irritation, and itching, which can exacerbate existing conditions.
4.2 Best Practices for Anal Hygiene
- Gentle Cleansing: Use gentle, fragrance-free wipes or warm water to clean the anal area after each bowel movement. Avoid harsh soaps, as they can cause irritation.
- Avoiding Excessive Wiping: Excessive wiping or rubbing can lead to skin irritation, especially in individuals with hemorrhoids or anal fissures.
- Use of Sitz Baths: Soaking in warm water can help alleviate discomfort and promote healing of the rectal area after bowel movements.
4.3 Avoiding Irritants
Certain products, such as scented toilet paper, creams, or soaps, can irritate the delicate skin around the anus. Opt for hypoallergenic and fragrance-free products to minimize irritation.
5. Stress Management and Mental Health
5.1 The Connection Between Stress and Rectal Health
Chronic stress can negatively affect the digestive system, leading to issues such as IBS, constipation, and even hemorrhoids. Stress can also increase muscle tension, which may worsen rectal discomfort.
5.2 Effective Stress-Relief Techniques
Managing stress is crucial for overall health, including rectal health. Techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, yoga, and regular physical activity can help reduce stress and improve digestive function.
5.3 The Role of Sleep in Gut Health
Adequate sleep is vital for maintaining a healthy digestive system. Poor sleep habits can exacerbate stress, disrupt digestion, and contribute to the development of rectal disorders. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night to support both mental and physical health.
6. Regular Medical Checkups and Screening
6.1 Importance of Regular Checkups
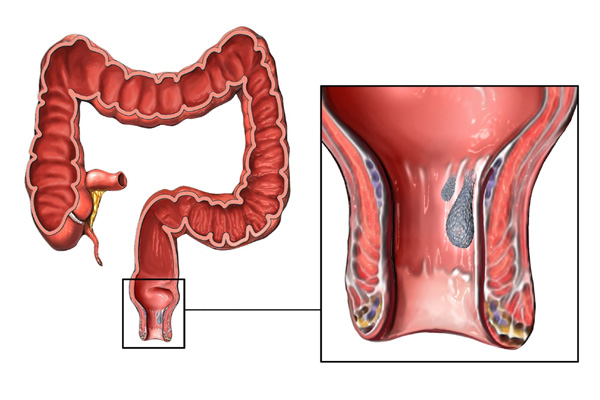
Regular medical checkups are crucial for identifying potential rectal issues early and preventing more severe complications. Routine screenings, such as colonoscopies or rectal exams, can detect conditions like colorectal cancer, which may not show symptoms in the early stages.
6.2 Recommended Screenings
- Colonoscopies: The gold standard for detecting colorectal cancer and other abnormalities in the colon and rectum. The American Cancer Society recommends that adults start screening at age 45, but individuals with a family history of colorectal cancer may need to begin earlier.
- Rectal Examinations: These are essential for diagnosing conditions like hemorrhoids, anal fissures, or rectal prolapse.
6.3 Early Intervention for Rectal Disorders
Timely medical intervention is key to managing rectal disorders effectively. Early diagnosis of conditions such as hemorrhoids, anal fissures, or colorectal cancer can lead to more successful treatment outcomes.
Maintaining rectal health is essential for overall well-being and quality of life. By adopting a healthy diet rich in fiber, staying hydrated, exercising regularly, practicing good hygiene, and managing stress, individuals can protect themselves from common rectal disorders. Additionally, regular medical checkups and early intervention play a significant role in preventing more serious conditions, such as colorectal cancer.
Taking proactive steps to maintain rectal health can not only prevent discomfort and pain but also reduce the risk of developing severe health problems. By implementing the measures outlined in this article, you can ensure better rectal health and enhance your overall quality of life.