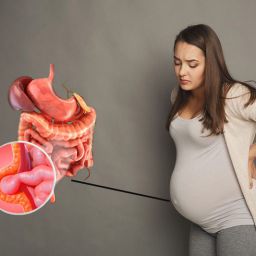
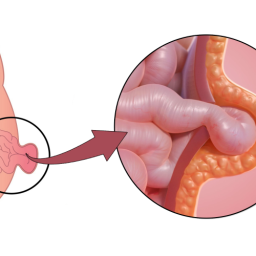
Understanding Recurrent Hernias
Before delving into the surgical methods for treating recurrent hernias, it is important to understand what a recurrent hernia is and why it occurs.
What is a Recurrent Hernia?
A recurrent hernia refers to a hernia that appears again at or near the site of a previous hernia repair. This can happen for various reasons, such as poor healing, the failure of the initial repair, or the development of new weak spots in the abdominal wall.
Causes of Recurrent Hernias

- Failure of Initial Surgery: One of the most common causes of hernia recurrence is the failure of the initial surgery. This can happen if the repair was not properly done or if the mesh used in the procedure did not adhere properly.
- Infection: If the area around the hernia becomes infected, it can prevent proper healing, leading to recurrence.
- Obesity: Excess weight places additional strain on the abdominal wall, increasing the likelihood of recurrence.
- Strenuous Activity: Lifting heavy objects or engaging in activities that place pressure on the abdomen can lead to hernia recurrence.
- Age and Health Conditions: Older adults or individuals with conditions that affect tissue healing may have a higher risk of hernia recurrence.
Symptoms of Recurrent Hernias
- A bulge at the surgical site
- Pain or discomfort, especially when lifting or bending
- Swelling or a feeling of heaviness in the abdominal area
- Tenderness or soreness at the repair site
Surgical Approaches to Treat Recurrent Hernia
Recurrent hernias require careful evaluation and a well-planned surgical approach. The surgical treatment of recurrent hernias is often more complex than the first repair due to scar tissue, changes in the abdominal wall, and other factors.
a. Open Hernia Repair
Open hernia repair is the traditional approach to hernia surgery, where the surgeon makes a large incision to access the hernia and surrounding tissues. In the case of recurrent hernias, open repair is often preferred because it allows for better visualization of the area, the identification of scar tissue, and the use of additional reinforcement, such as mesh.
Procedure Overview:
- Incision: The surgeon makes an incision near the previous surgical site to expose the hernia.
- Exposing the Hernia: The herniated tissue is gently pushed back into the abdominal cavity.
- Reinforcing the Abdominal Wall: A mesh is typically used to reinforce the weakened area of the abdominal wall. In recurrent hernias, the surgeon may opt for a larger mesh to ensure a more robust repair.
- Closing the Incision: The incision is closed, and the healing process begins.
Advantages:
- Provides direct access to the hernia site.
- Effective for large or complex recurrent hernias.
- Allows the use of reinforcing materials like mesh.
Disadvantages:
- Larger incision and longer recovery time compared to minimally invasive techniques.
- Higher risk of wound infections or complications due to the larger surgical site.
b. Laparoscopic (Minimally Invasive) Hernia Repair
Laparoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive option for treating recurrent hernias. It involves using small incisions and specialized instruments to repair the hernia. Laparoscopic surgery is often considered for recurrent hernias, particularly in individuals who are otherwise healthy and prefer a faster recovery.
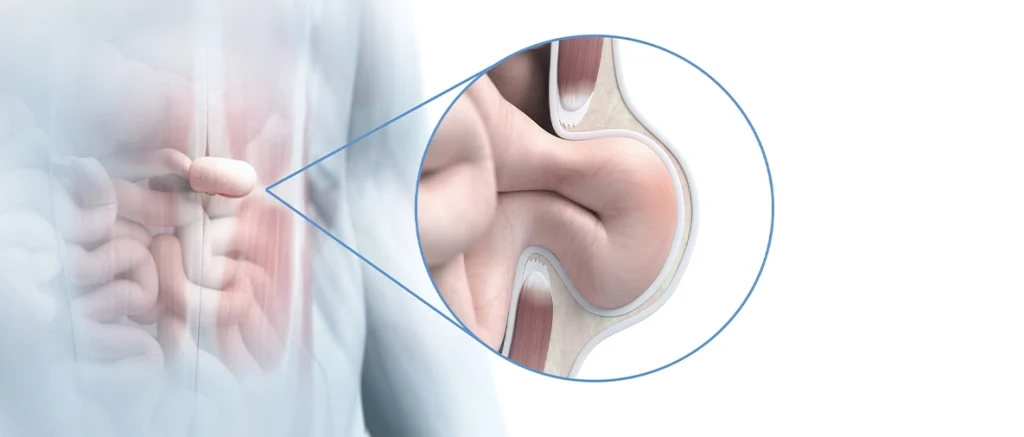
Procedure Overview:
- Small Incisions: Several small incisions are made in the abdominal area.
- Insertion of the Camera and Instruments: A tiny camera (laparoscope) is inserted through one of the incisions to provide real-time images of the surgical site. Specialized instruments are used to push the herniated tissue back into place and reinforce the abdominal wall.
- Mesh Placement: As with open surgery, mesh is placed over the weakened area to prevent the hernia from returning.
- Closing the Incisions: The small incisions are closed with stitches.
Advantages:
- Smaller incisions, leading to reduced scarring and pain.
- Faster recovery time and shorter hospital stay.
- Lower risk of wound infections compared to open surgery.
Disadvantages:
- Not suitable for large or very complex hernias.
- Requires specialized equipment and skilled surgeons.
- Longer procedure time compared to open surgery.
c. Robotic-Assisted Hernia Repair
Robotic-assisted surgery is an advanced form of laparoscopic surgery that uses robotic systems to aid the surgeon in performing the operation. It provides a high level of precision and control, making it an effective option for treating recurrent hernias.
Procedure Overview:
- Small Incisions: As with laparoscopic surgery, small incisions are made.
- Robotic Assistance: The surgeon operates robotic arms that hold surgical instruments and a camera. The robotic system provides enhanced visualization and greater precision in repairing the hernia.
- Mesh Placement: The surgeon places mesh over the weakened abdominal wall to reinforce it.
- Closing the Incisions: The incisions are closed once the repair is completed.
Advantages:
- High precision and control, leading to better outcomes.
- Minimally invasive with smaller incisions.
- Faster recovery and reduced risk of complications.
Disadvantages:
- Requires specialized robotic equipment and a highly skilled surgeon.
- May not be widely available in all healthcare settings.
- Higher cost compared to traditional laparoscopic surgery.
Considerations and Challenges in Recurrent Hernia Surgery
Surgical repair of recurrent hernias presents several challenges that must be carefully addressed:
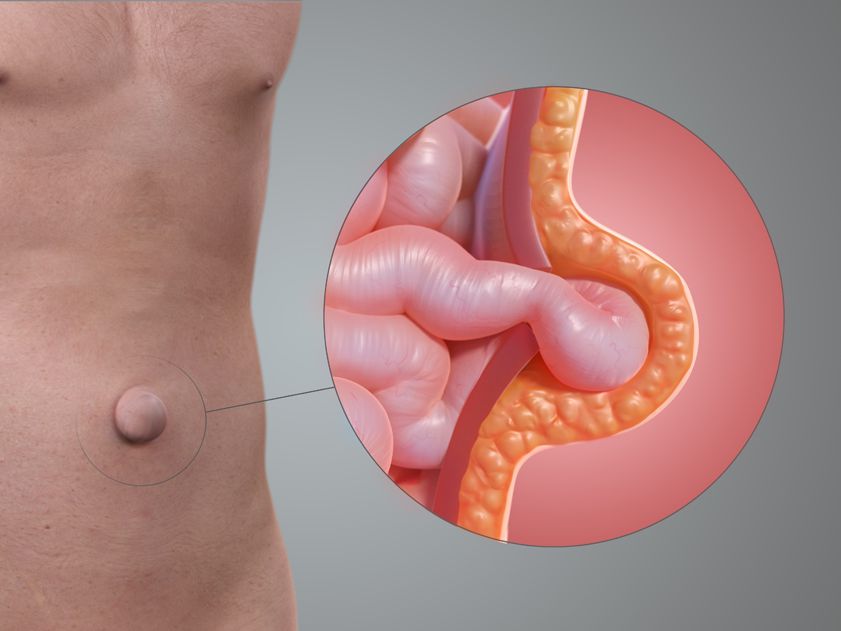
a. Scar Tissue and Adhesions
Recurrent hernias often involve significant scar tissue from previous surgeries. This can make the surgery more complex and increase the risk of injury to nearby structures, such as the intestines or blood vessels. Surgeons must carefully navigate this scar tissue to avoid complications.
b. Mesh Selection
In recurrent hernia surgeries, the selection of an appropriate mesh is critical. Surgeons may opt for larger or more durable mesh to ensure that the repair is robust enough to withstand the pressure of future activity. The type of mesh used may vary depending on the size of the hernia, the patient’s health, and the location of the hernia.
c. Risk of Infection
Infections are a concern in any surgery, but they are especially problematic in recurrent hernia repair. The presence of scar tissue and previous surgical wounds increases the risk of infection. Surgeons may take extra precautions, such as using antibiotic prophylaxis and employing careful wound management techniques.
Recovery and Post-Surgical Care
Recovery from recurrent hernia surgery varies depending on the type of surgery performed and the patient’s overall health.
Post-Operative Care:
- Pain Management: Pain medications are prescribed to manage discomfort during the recovery period. Most patients experience mild to moderate pain that improves after a few days.
- Activity Restrictions: Patients are advised to avoid strenuous activities, heavy lifting, or intense physical exertion for several weeks to prevent the risk of further hernia formation.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Regular follow-up visits are necessary to monitor the healing process and ensure that the hernia repair is successful.
Recovery Time:
- Open Surgery: Recovery from open surgery typically takes 4-6 weeks, with the patient advised to avoid heavy lifting for at least 6 weeks.
- Laparoscopic Surgery: Laparoscopic surgery usually results in a quicker recovery, with most patients returning to normal activities within 1-2 weeks.
- Robotic-Assisted Surgery: Similar to laparoscopic surgery, robotic-assisted surgery offers a faster recovery with less pain and scarring.
Recurrent hernias present a significant challenge for both patients and surgeons. While many of these hernias can be effectively treated with surgical intervention, the type of surgery chosen depends on factors such as the size and complexity of the hernia, the patient’s health, and the surgical approach used in the previous repair. Open, laparoscopic, and robotic-assisted surgeries are all viable options for treating recurrent hernias, each with its advantages and considerations.
For patients experiencing recurrent hernias, working closely with a skilled surgeon to determine the best surgical approach is crucial to achieving successful outcomes. Additionally, lifestyle changes and proper post-operative care can help reduce the risk of further recurrence and ensure long-term health.