1. Understanding Umbilical Hernia and Its Symptoms
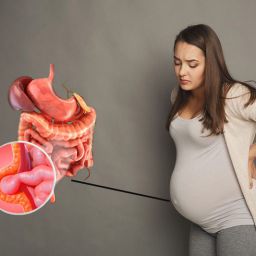
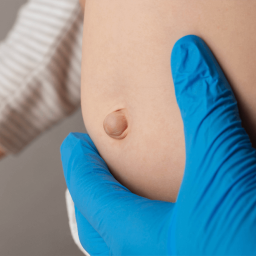
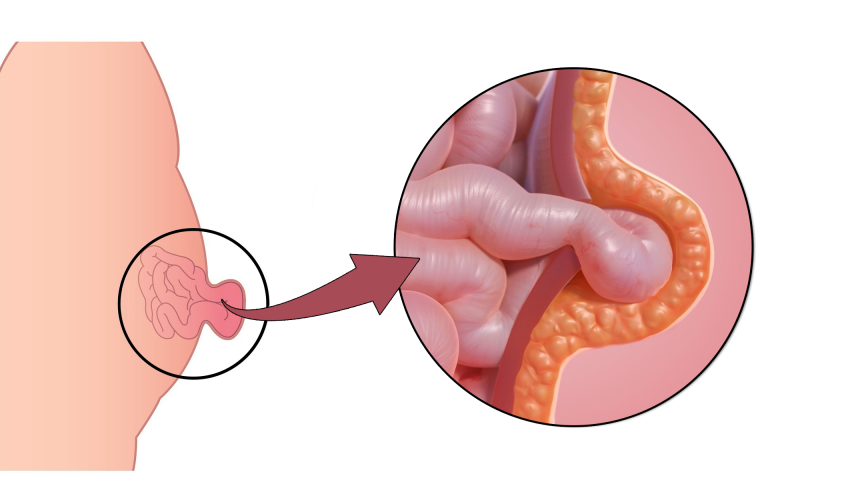
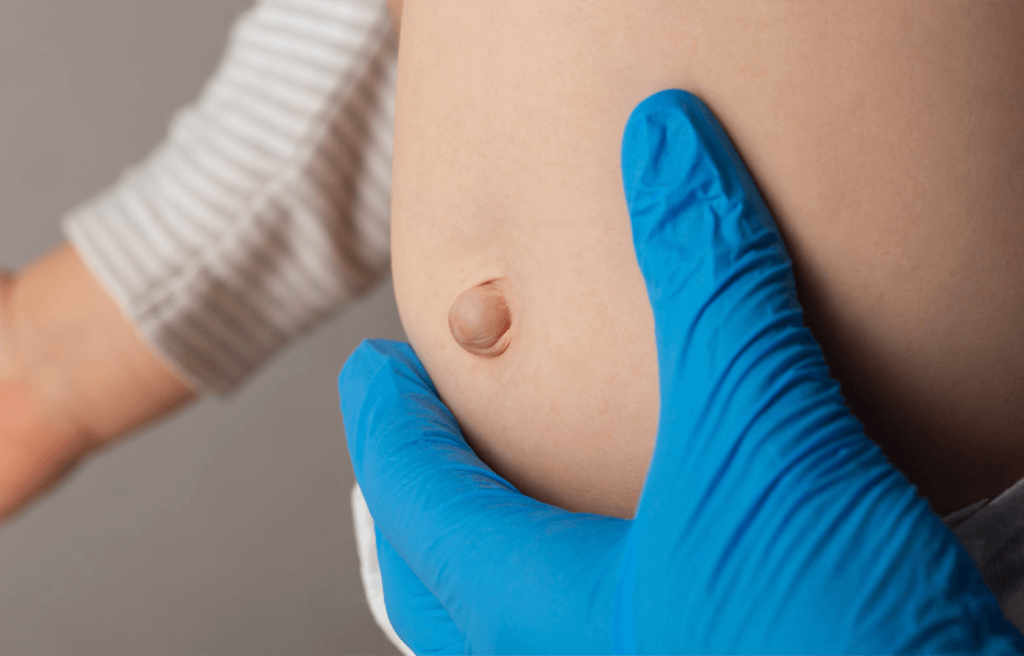
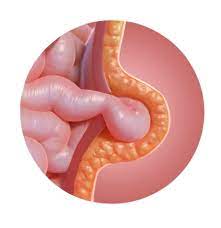
Before diving into relaxation methods, it is essential to understand the condition itself and the symptoms it presents. An umbilical hernia occurs when a part of the intestine or fatty tissue pushes through the abdominal wall near the navel. It is most common in infants, but adults can also develop this condition.
- Common Symptoms of Umbilical Hernia:
- A visible bulge near the belly button that may become more pronounced when coughing or straining.
- Mild to moderate pain or discomfort around the bulging area, especially during physical activity or when lifting heavy objects.
- Tenderness or aching at the site of the hernia, particularly after prolonged periods of standing or walking.
While the bulge can sometimes resolve on its own, it can cause ongoing discomfort and pain. Relaxation techniques can be particularly useful for managing these symptoms in the interim.
2. The Importance of Relaxation for Individuals with Umbilical Hernia
Relaxation techniques are vital in helping individuals with umbilical hernias reduce muscle tension, ease pain, and manage the stress that can be associated with chronic discomfort. These techniques help to activate the body’s natural relaxation response, which can alleviate pain, lower anxiety, and improve sleep quality. For individuals with umbilical hernias, effective relaxation can also reduce the pressure on the abdominal wall and promote overall well-being.
Here are some key benefits of relaxation for those dealing with an umbilical hernia:
- Pain Management: Relaxation techniques can help manage pain by reducing muscle tension and stimulating the body’s natural pain-relieving mechanisms.
- Stress Reduction: Dealing with a hernia can be frustrating and stressful. Relaxation methods help decrease anxiety and improve mental clarity.
- Improved Mobility: Relaxation can help with improving flexibility and range of motion, making it easier for individuals to carry out daily tasks without exacerbating symptoms.
- Better Sleep: Many individuals with an umbilical hernia experience disrupted sleep due to discomfort. Relaxation techniques help improve sleep quality and reduce discomfort during rest.
3. Physical Relaxation Techniques for Umbilical Hernia Relief
Physical relaxation methods are one of the most effective ways to manage the symptoms of an umbilical hernia. These methods focus on relieving tension in the muscles around the abdominal wall and supporting the body’s overall flexibility and comfort.
a. Gentle Stretching Exercises
Gentle stretching exercises can help relieve muscle tension around the abdominal area and lower back, which is crucial for individuals with an umbilical hernia. Regular stretching can also prevent stiffness and improve posture, both of which help reduce the strain on the hernia.
- How to Stretch Safely:
- Focus on slow, controlled movements that do not place undue pressure on the abdomen.
- Perform stretches that target the back, legs, and core muscles, as these areas help stabilize the abdomen and reduce pressure on the hernia site.
- Avoid any stretches that involve heavy lifting or forceful movements.
Common stretches that may help include:
- Seated Forward Bend: This stretch targets the hamstrings and lower back and helps release tension in the body.
- Cat-Cow Stretch: This gentle stretch helps promote spinal flexibility and alleviates pressure in the abdomen.
- Side Stretch: This stretch helps open the rib cage and torso, reducing pressure on the abdominal wall.
b. Deep Breathing Exercises
Deep breathing exercises are a simple yet highly effective way to reduce tension, manage pain, and promote relaxation. By focusing on slow, controlled breathing, individuals can activate the parasympathetic nervous system (the body’s relaxation response), which helps reduce stress and alleviate abdominal discomfort.
- How to Perform Deep Breathing:
- Sit or lie down in a comfortable position.
- Place one hand on your chest and the other on your abdomen.
- Inhale deeply through your nose, allowing your diaphragm to expand fully and your abdomen to rise. Exhale slowly through your mouth.
- Aim for 5-10 minutes of deep breathing per session to experience full relaxation benefits.
c. Heat and Cold Therapy
Using heat or cold on the affected area can help relax muscles and alleviate discomfort caused by the hernia. Heat therapy can promote blood flow and muscle relaxation, while cold therapy can reduce inflammation and numb pain.
- How to Apply Heat or Cold Therapy:
- Heat Therapy: Apply a warm compress or heating pad to the lower abdomen to relieve muscle tension and promote relaxation. Be sure not to apply heat directly to the skin; wrap the heat source in a cloth to avoid burns.
- Cold Therapy: If the hernia is inflamed or swollen, using an ice pack wrapped in a cloth can help reduce swelling and numb pain. Apply cold for 15-20 minutes at a time, ensuring that the skin is protected from direct contact with ice.
4. Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
Mindfulness and mental relaxation techniques are powerful tools for managing stress and alleviating the discomfort associated with an umbilical hernia. These practices help individuals focus on the present moment, which can reduce anxiety and promote a sense of calm.
a. Meditation
Meditation has been shown to reduce stress, improve focus, and help manage chronic pain. Guided meditation sessions, particularly those that focus on body scanning and abdominal relaxation, can be particularly effective for individuals with an umbilical hernia.
- How to Meditate:
- Find a quiet space and sit comfortably.
- Close your eyes and focus on your breath, taking slow, deep breaths.
- If your mind begins to wander, gently bring your focus back to your breath or a mantra.
- You can also try body scan meditation, where you mentally scan each part of your body, focusing on areas of tension and encouraging them to relax.
b. Progressive Muscle Relaxation (PMR)
Progressive muscle relaxation is a technique that involves tensing and then relaxing various muscle groups throughout the body. This helps release tension, increase body awareness, and promote deep relaxation.
- How to Practice PMR:
- Start at your feet and work your way up to your head.
- Tense each muscle group for a few seconds, then release and relax.
- Focus on the contrast between tension and relaxation in each area.
5. Lifestyle Adjustments to Support Relaxation
Certain lifestyle adjustments can complement relaxation techniques and help support individuals with an umbilical hernia in managing their symptoms.
- Maintaining a Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in fiber can help prevent constipation, which can worsen the symptoms of an umbilical hernia. Avoiding heavy, fatty, or spicy foods may also help reduce discomfort.
- Regular Exercise: While strenuous activities should be avoided, low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, and yoga can strengthen core muscles and improve overall mobility.
- Managing Stress: Stress can exacerbate the discomfort caused by an umbilical hernia. Engaging in regular stress management practices such as yoga, journaling, or talking to a counselor can help alleviate emotional strain.
6. When to Seek Medical Attention
While relaxation methods can help manage symptoms, it’s important to seek medical attention if the hernia becomes increasingly painful, if there is a noticeable change in size or appearance, or if complications such as strangulation occur. In these cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair the hernia and prevent further complications.
While living with an umbilical hernia can be challenging, there are numerous methods available to support relaxation, alleviate pain, and manage symptoms effectively. Gentle stretching, deep breathing exercises, heat and cold therapy, mindfulness techniques, and lifestyle adjustments can all contribute to a better quality of life for individuals dealing with this condition. By incorporating these methods into their daily routine, individuals can reduce the discomfort of an umbilical hernia and promote overall health and well-being until they are able to receive the appropriate medical treatment.