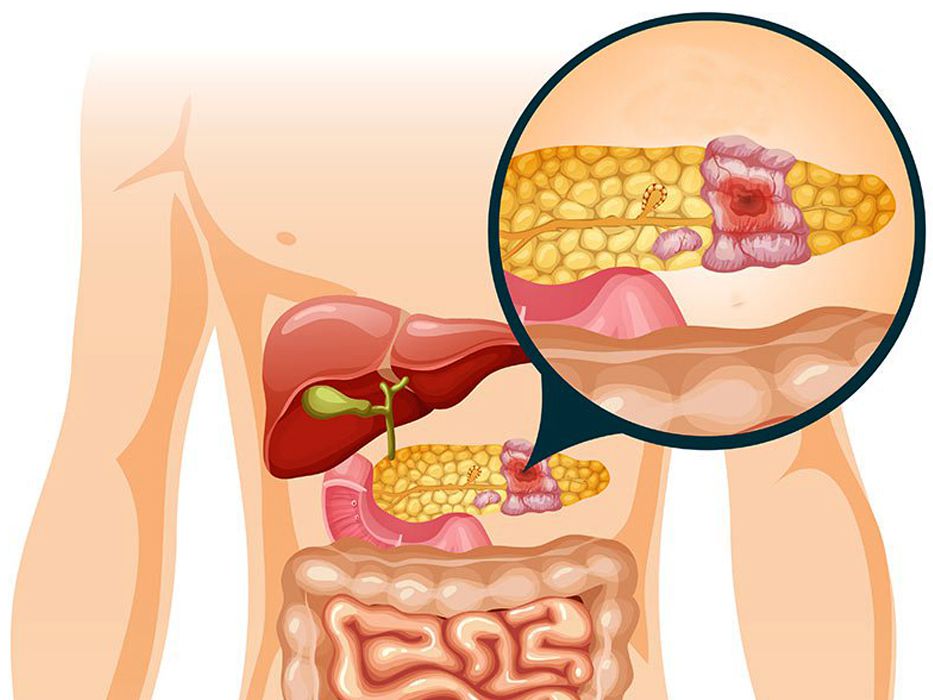
1. Surgical Complications After Pancreatic Cancer Surgery
Surgical treatment for pancreatic cancer is often necessary, especially if the tumor is operable. The most common surgery for pancreatic cancer is the Whipple procedure (pancreaticoduodenectomy), which involves the removal of the head of the pancreas, part of the small intestine, the gallbladder, and the bile duct. While surgery can improve survival rates, it is a complex procedure with the potential for significant complications.
1.1 Infection and Wound Healing Issues
After any major surgery, infection is a potential risk. In pancreatic cancer surgery, infection may occur in the surgical site or in internal organs due to the complexity of the procedure. Patients may experience:
- Fever: An early sign of infection.
- Redness, Swelling, or Drainage: Around the incision site.
- Intra-abdominal Abscesses: These are collections of pus that may form inside the abdomen, requiring drainage and sometimes additional surgery.
Effective post-surgery wound care and prompt attention to signs of infection can help mitigate these risks.
1.2 Pancreatic Fistula
A pancreatic fistula is an abnormal connection between the pancreas and other organs or tissues, resulting in leakage of pancreatic enzymes into the abdominal cavity. This condition can cause severe inflammation, infection, and damage to surrounding organs. Signs of a pancreatic fistula may include:
- Persistent Drainage: Of a brownish, foul-smelling fluid from the surgical site.
- Fever and Abdominal Pain: Due to infection or irritation.
Treatment often involves draining the fluid and sometimes additional surgical intervention.
1.3 Delayed Gastric Emptying
Another common complication after pancreatic surgery is delayed gastric emptying, where food moves too slowly from the stomach to the small intestine. This can lead to:
- Nausea and Vomiting: Due to food not passing through the digestive tract properly.
- Loss of Appetite: Leading to malnutrition and dehydration.
- Abdominal Distension: Bloating due to a backup of food and fluids.
This condition can improve over time, but some patients may require medical or dietary interventions to manage symptoms.
2. Chemotherapy-Related Complications
Chemotherapy is a common treatment for pancreatic cancer, either as a primary treatment or as part of an adjuvant therapy plan after surgery. While chemotherapy can be effective in controlling the disease and preventing recurrence, it comes with a variety of potential side effects and complications.
2.1 Nausea and Vomiting
Chemotherapy can trigger nausea and vomiting, which are among the most common side effects. This can significantly affect a patient’s ability to maintain proper nutrition, leading to:
- Weight Loss: Due to a lack of appetite and difficulty eating.
- Dehydration: Caused by vomiting and reduced fluid intake.
Antiemetic medications are commonly prescribed to manage nausea and vomiting, but in some cases, patients may need to adjust their diet or eating habits to minimize symptoms.
2.2 Fatigue
Fatigue is one of the most common chemotherapy side effects. The treatment can disrupt normal cell function and impair the body’s ability to recover, leading to:
- Extreme Tiredness: That does not improve with rest.
- Difficulty Performing Daily Activities: Fatigue can severely impact a patient’s quality of life.
Fatigue management strategies include pacing activities, rest, and ensuring adequate nutrition and hydration.
2.3 Neuropathy
Chemotherapy drugs, particularly gemcitabine and oxaliplatin, can cause peripheral neuropathy, a condition where nerves in the hands and feet become damaged. This leads to:
- Tingling or Numbness: In the fingers and toes.
- Weakness: In the hands and feet, making it difficult to perform tasks.
- Pain: That may worsen over time.
Neuropathy management often involves reducing chemotherapy dosages, using medications to alleviate pain, and physical therapy.
3. Radiation Therapy-Related Complications
Radiation therapy, though less commonly used for pancreatic cancer, may be employed in certain cases to shrink tumors or treat metastatic lesions. However, radiation can lead to various complications, especially if the tumor is near sensitive organs like the liver, stomach, or intestines.
3.1 Fatigue and Skin Reactions
Fatigue is also common with radiation therapy, similar to chemotherapy. Additionally, skin reactions like redness, irritation, or peeling can occur in the treated area. These reactions typically resolve after treatment is completed but can cause discomfort in the meantime.
3.2 Gastrointestinal Issues
Radiation can cause inflammation of the intestines, leading to:
- Nausea and Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Bloating or Abdominal Cramping
These symptoms can affect digestion and the patient’s ability to absorb nutrients.
4. Long-Term Complications After Pancreatic Cancer Treatment
In addition to the immediate complications that may arise from surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy, patients may experience long-term issues that affect their recovery and overall health.
4.1 Diabetes
The pancreas plays a key role in regulating blood sugar levels through insulin production. Surgical removal of part or all of the pancreas can result in the development of diabetes, especially if the insulin-producing cells are affected. This can lead to:
- Increased Thirst and Urination
- Fatigue
- Uncontrolled Blood Sugar Levels
Diabetes management may include insulin therapy, dietary changes, and regular blood sugar monitoring.
4.2 Malnutrition and Weight Loss
Because the pancreas also aids in digestion through the secretion of enzymes, surgery that affects the pancreas can result in malabsorption. This leads to difficulty absorbing nutrients from food, resulting in:
- Unexplained Weight Loss
- Fatigue
- Weakness
Pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy (PERT) is often prescribed to aid digestion and improve nutrient absorption.
4.3 Psychological Effects
The psychological toll of battling pancreatic cancer, coupled with the physical challenges, can lead to long-term mental health issues such as:
- Depression: Due to the emotional stress of living with cancer and its complications.
- Anxiety: About recurrence and ongoing treatment.
- Post-Traumatic Stress: After major surgery or the emotional strain of aggressive treatments.
Psychological support, including counseling, therapy, and support groups, is often necessary to help patients cope with the emotional burden of their illness.
Pancreatic cancer treatment can cause a wide range of complications that significantly impact patients’ quality of life. Surgical complications, chemotherapy side effects, radiation-related issues, and long-term health problems like diabetes and malnutrition are all common hurdles that patients must navigate during their recovery.
However, with proper management, medical intervention, and psychological support, many of these complications can be controlled or mitigated, allowing patients to regain some level of normalcy in their lives. Ongoing communication with healthcare providers is crucial to ensuring that complications are identified early and treated promptly, improving both survival rates and quality of life.