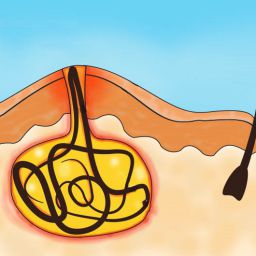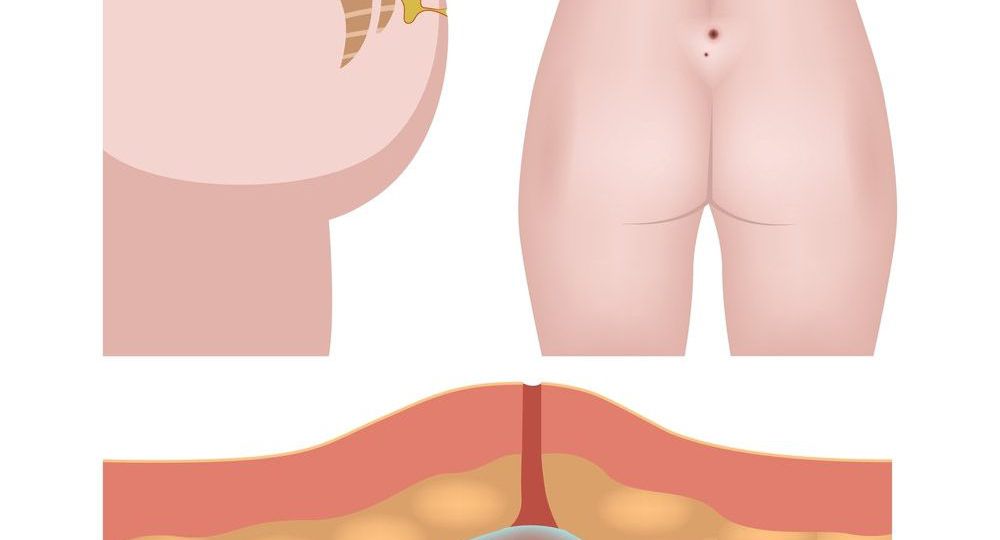
Is There a Genetic Predisposition for Pilonidal Sinus?
Pilonidal sinus is widely recognized as an acquired condition, primarily influenced by external factors like trauma, poor hygiene, and prolonged pressure in the area. However, a growing body of research suggests that genetics might play a role in making some individuals more susceptible to the condition.
Family History and Pilonidal Sinus
Studies have shown that individuals with a family history of pilonidal sinus may have an increased likelihood of developing the condition. Several studies have indicated a higher prevalence of pilonidal sinus among first-degree relatives (such as parents and siblings) of individuals affected by the condition. This suggests that genetic factors could contribute to an individual’s susceptibility.
A 2015 study published in the Journal of the American College of Surgeons explored the hereditary nature of pilonidal sinus. The study found that patients with a family history of pilonidal sinus were more likely to experience the condition, indicating a potential genetic link. This familial clustering suggests that there may be certain genetic factors that predispose individuals to develop pilonidal sinus, although the exact genes involved remain unclear.
Genetic Factors Involved in Pilonidal Sinus Development
Genetic predisposition refers to an individual’s inherited genetic makeup that increases their risk of developing certain diseases. The specific genetic components involved in pilonidal sinus are still being researched, but several hypotheses have been proposed based on familial trends and patterns observed in clinical settings.
- Skin Structure and Hair Follicles: Pilonidal sinus often develops as a result of ingrown hairs or hair follicle infection. Genetics could influence the density, size, or growth pattern of hair follicles, particularly in the sacrococcygeal region. People with denser hair growth may be more prone to developing ingrown hairs, which could lead to the formation of a pilonidal sinus. Familial tendencies toward excessive hair growth in certain areas of the body have been noted, which could contribute to the condition’s recurrence.
- Collagen Production and Skin Integrity: Genetic factors may also influence the body’s production of collagen, the protein responsible for maintaining the structure and integrity of the skin. Variations in collagen production could make the skin more prone to developing pits or sinuses. Research into connective tissue disorders and their potential link to pilonidal sinus is still in its early stages, but it could offer insight into the genetic influences that affect skin healing and tissue structure.
- Inflammatory Response: The body’s inflammatory response could be another area where genetics plays a role. In some individuals, the immune system may react more strongly to trauma or ingrown hairs, increasing the likelihood of infection and the formation of a pilonidal sinus. A hereditary predisposition to certain immune system responses could make some people more vulnerable to developing the condition.
- Anatomical Factors: Family history can also contribute to certain anatomical features that may predispose individuals to pilonidal sinus. For example, individuals with a deeper natal cleft or certain variations in sacrococcygeal anatomy may be more prone to the condition. Genetic factors influencing the development of these anatomical features may explain the familial clustering of pilonidal sinus cases.
Environmental vs. Genetic Factors
While genetics may play a role, environmental and lifestyle factors are also critical in the development of pilonidal sinus. It is important to note that genetics likely does not act alone but in combination with other factors.
Risk Factors for Pilonidal Sinus
Some of the common environmental and lifestyle risk factors for pilonidal sinus include:
- Prolonged sitting or pressure: Individuals who sit for long periods, especially those with jobs that require long hours of sitting (e.g., truck drivers, office workers), are at higher risk.
- Obesity: Overweight or obese individuals may have increased pressure on the sacrococcygeal area, contributing to the development of the condition.
- Excessive hair growth: As mentioned earlier, excessive hair in the sacrococcygeal region can increase the likelihood of ingrown hairs, which can lead to pilonidal sinus.
- Poor hygiene: Inadequate hygiene in the buttocks region may lead to increased bacterial growth and the risk of infection.
- Trauma or injury: A direct injury to the area or repeated friction can increase the likelihood of developing a pilonidal sinus.
These risk factors, when combined with a genetic predisposition, may significantly increase the chances of developing pilonidal sinus.
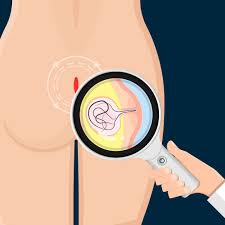
Diagnosis and Treatment of Pilonidal Sinus
Regardless of whether there is a genetic predisposition, early diagnosis and treatment of pilonidal sinus are crucial in preventing complications. Pilonidal sinus is usually diagnosed through a physical examination, and imaging may be performed if there are concerns about underlying infection or abscesses.
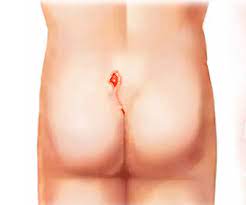
Treatment options for pilonidal sinus include:
- Conservative Management: For mild cases, lifestyle changes such as improved hygiene, hair removal, and avoiding prolonged sitting may help manage the condition. Warm sitz baths can also reduce discomfort.
- Antibiotics: If an infection is present, antibiotics may be prescribed to treat the underlying infection and prevent further complications.
- Surgical Intervention: In more severe cases or when the condition becomes chronic, surgery may be necessary. Surgical options include drainage of abscesses, excision of the sinus tract, or more complex procedures such as flap surgery or laser treatment.
- Postoperative Care: After surgery, patients are advised to maintain proper hygiene and avoid prolonged sitting to reduce the risk of recurrence. In some cases, lifestyle changes, including weight management, may be recommended.
Pilonidal sinus is a common condition that can have a significant impact on quality of life. While the primary causes of pilonidal sinus include environmental and lifestyle factors, there is evidence to suggest that genetics may play a role in increasing the likelihood of developing the condition. Family history and genetic predisposition, such as hair growth patterns, collagen production, and anatomical variations, may influence the development of pilonidal sinus.
However, environmental factors such as prolonged sitting, obesity, and poor hygiene should not be overlooked, as they significantly contribute to the onset and recurrence of pilonidal sinus. Understanding both the genetic and environmental factors that influence pilonidal sinus can help individuals reduce their risk and seek timely treatment if needed.