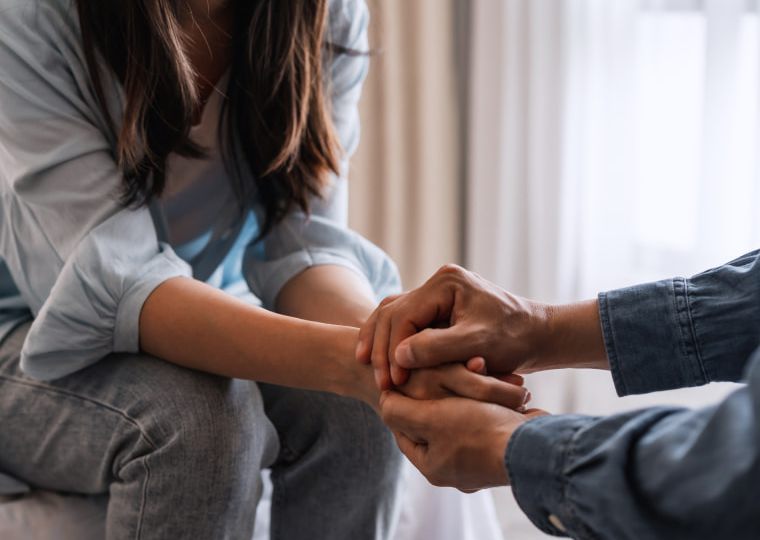
Understanding the Emotional Impact of Organ Transplantation
Undergoing an organ transplant is not only a physical transformation but also a profound emotional and psychological experience. Patients may experience a wide range of emotions, such as relief, fear, gratitude, anxiety, and sadness. The adjustment period after transplantation can be emotionally challenging due to several factors, including:

- Fear of Rejection: Patients are often worried about their body’s rejection of the new organ. The possibility that the body may not accept the transplanted organ, which could lead to complications, is a common source of anxiety.
- Grief and Survivor’s Guilt: Organ transplant recipients may feel guilt because their transplant was made possible by the death of a donor. They may also struggle with the loss of their previous lifestyle or the emotional burden of the transplant process itself.
- Depression and Anxiety: The uncertainty associated with organ transplants, the risk of complications, and the stress of managing a long-term treatment plan can contribute to feelings of depression and anxiety.
- Body Image and Identity Changes: After a transplant, patients may have scars, changes in appearance, or altered bodily functions that can affect their sense of identity and self-esteem.
- Post-Traumatic Stress: The physical and emotional stress of undergoing a transplant can be traumatic. Patients may experience flashbacks, nightmares, or intrusive thoughts about their medical experiences.
These emotional and psychological reactions are completely normal and part of the human experience of going through such a major medical procedure. However, without adequate support, these feelings can overwhelm patients, affecting their ability to recover both physically and emotionally.
The Role of Psychological Support in the Post-Transplant Period
Psychological support refers to the assistance provided by mental health professionals to help individuals navigate the emotional challenges associated with health conditions and medical procedures. After an organ transplant, psychological support helps patients manage the emotional toll of their condition and improves overall health outcomes.
Psychological support is essential for several reasons:
- Coping with Anxiety and Fear: Patients who receive counseling or therapy can learn effective coping strategies to manage their anxiety. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), for example, helps patients address irrational thoughts and replace them with healthier perspectives, reducing their stress levels.
- Addressing Depression: Organ transplant recipients are at a higher risk for developing depression due to the intense emotional strain of the transplant process. Psychological support can help them identify signs of depression early and provide intervention strategies to improve their mental health.
- Improving Adherence to Medication: Organ transplant patients must adhere to a strict regimen of immunosuppressive drugs to prevent organ rejection. Psychological support can help patients overcome the emotional barriers that make it difficult to consistently follow their medication plan, such as depression or anxiety about the side effects of the drugs.
- Promoting Positive Mental Health: Having access to psychological support can help individuals focus on the positives in their lives. By addressing the emotional challenges associated with transplantation, patients can cultivate resilience, improve their outlook on life, and enhance their mental well-being.
- Enhancing Quality of Life: Organ transplant patients are often dealing with complex medical conditions, which can negatively impact their quality of life. Psychological support can help improve patients’ self-esteem, body image, and self-worth, allowing them to live fuller, more meaningful lives post-transplant.
When Is Psychological Support Recommended?
Psychological support is not just a generalized need for all organ transplant patients; it is often recommended based on specific circumstances and individual needs. The recommendation for psychological support can be influenced by various factors, including the patient’s emotional response to the transplant process, their pre-existing mental health conditions, and the medical complexity of their transplant.
Here are some situations in which psychological support is strongly recommended:
1. Pre-Transplant Psychological Evaluation
Before an organ transplant is even performed, patients may undergo a psychological evaluation. This pre-transplant psychological assessment is designed to identify any underlying emotional or mental health concerns that could affect the success of the transplant. Identifying psychological challenges early on helps ensure that the patient is mentally prepared for the transplant journey. Some common conditions identified during this assessment include:
- Severe anxiety or depression that might interfere with the patient’s ability to engage in post-transplant care.
- Unrealistic expectations about the outcome of the transplant or an unwillingness to follow medical advice.
- Previous trauma or mental health issues that could make adjusting to the transplant more difficult.
Addressing these issues before the transplant helps minimize complications and ensures better adherence to treatment plans.
2. Post-Transplant Depression or Anxiety
One of the most common reasons psychological support is recommended after a transplant is when patients develop depression or anxiety. The stress and emotional impact of the transplant process, coupled with the long recovery period, can trigger significant mental health struggles. These struggles may be compounded by:
- Changes in lifestyle: Patients may feel disconnected from their former selves as they adjust to life after the transplant. They might need time to process their feelings of vulnerability and dependence on others.
- Physical recovery challenges: The physical side effects of the transplant, including fatigue, weight changes, and immunosuppressant medication side effects, can worsen mental health conditions.
In such cases, counseling or therapy can be extremely beneficial in helping patients regain emotional balance and develop strategies to manage their symptoms.
3. Survivor’s Guilt
Survivor’s guilt is a common psychological issue faced by organ transplant recipients. The knowledge that their life was saved by the death of another person can lead to complex feelings of guilt, particularly when patients are aware that their donor’s family may be grieving. Survivor’s guilt can lead to feelings of shame, depression, or worthlessness.
Psychological support helps patients work through these emotions and understand that their survival is not a reflection of any wrongdoing but rather a gift. Therapy can help patients come to terms with these feelings, and grief counseling may be recommended to help process the donor’s death respectfully.
4. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) can develop after a major life-threatening medical procedure like an organ transplant. Some patients may experience intrusive memories of the transplant process, nightmares, and heightened anxiety related to the trauma of the experience. PTSD can significantly impact daily functioning, and it is crucial to address it with professional psychological support.
Treatment for PTSD may include techniques such as cognitive processing therapy (CPT) or eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR), both of which can help patients process traumatic memories and reduce symptoms of PTSD.
5. Difficulty Adapting to a New Lifestyle
Life after an organ transplant often requires significant lifestyle changes. Patients must take immunosuppressant medications, attend regular medical checkups, and maintain a healthy diet and exercise routine. These changes may be difficult to navigate without adequate psychological support. Patients may struggle with:
- Adherence to medication: Difficulty managing the side effects of immunosuppressants or fear of side effects can cause patients to resist taking their medications regularly, putting the success of the transplant at risk.
- Dietary restrictions: After transplantation, patients may be required to follow a strict diet to optimize their health and prevent complications. This can be stressful and overwhelming without the right support.
- Physical limitations: Post-transplant fatigue, pain, and physical limitations can lead to feelings of frustration, isolation, and low self-esteem.
In such situations, therapy or counseling can help patients adjust to their new lifestyle and develop effective coping mechanisms.
6. Family and Relationship Strain
The emotional and physical strain of undergoing a transplant can also affect relationships with family members and caregivers. Family members may experience their own emotional challenges, such as anxiety, stress, and fatigue. If these concerns are not addressed, they can lead to misunderstandings or strain in family dynamics.
Family therapy or support groups can help both patients and their loved ones navigate the emotional complexities of transplant recovery, fostering communication, understanding, and emotional support.
Psychological support plays a vital role in the recovery process after an organ transplant. From managing anxiety and depression to coping with survivor’s guilt and PTSD, emotional well-being is integral to the overall success of the transplant journey. In some cases, psychological support is needed before the transplant procedure to prepare the patient mentally, while in other cases, it is necessary afterward to address specific emotional challenges that arise during recovery.