1. Introduction to HIPEC Treatment
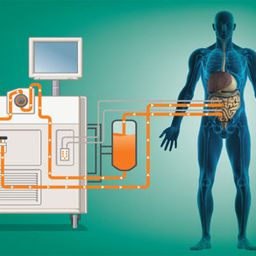
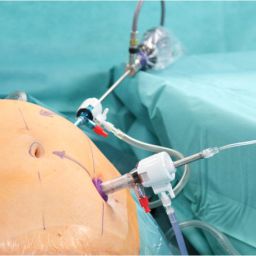
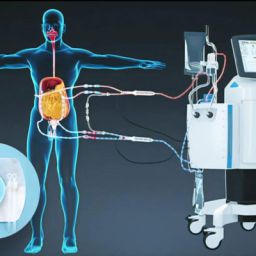
HIPEC, or Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy, is a procedure that delivers heated chemotherapy directly to the peritoneal cavity, which is the area surrounding the abdominal organs. This treatment is typically used after a surgeon removes visible tumors from the abdomen, allowing for a more targeted application of chemotherapy. By using heat, HIPEC enhances the effectiveness of chemotherapy drugs, which work to kill cancer cells and prevent further cancer growth and spread.
Unlike traditional intravenous chemotherapy, which circulates through the bloodstream and affects the entire body, HIPEC allows the drugs to be delivered directly to the site of the cancer. The heat further facilitates the penetration of the chemotherapy drugs into the tumor tissue, making it more effective.
2. The Mechanism of HIPEC: How It Works
HIPEC works by delivering a heated chemotherapy solution directly into the abdominal cavity after the removal of visible tumors. The primary mechanism behind this treatment involves:
- Heat Activation: The chemotherapy solution is heated to around 41 to 42 degrees Celsius (105.8 to 107.6 degrees Fahrenheit). The heat causes the cancer cells to become more sensitive to the chemotherapy drugs, improving their ability to kill cancer cells.
- Localized Treatment: By directly targeting the peritoneal cavity, HIPEC minimizes the systemic side effects of chemotherapy, such as nausea, fatigue, and hair loss. The localized treatment ensures that the drugs reach the cancer cells directly and kill them while leaving healthy tissues largely unaffected.
- Cytotoxicity Enhancement: The heat also helps increase the drug’s cytotoxic effects, making it more potent against the cancer cells. Cancer cells, when exposed to high temperatures, become more vulnerable to chemotherapy, which is why the combination of heat and chemotherapy can be highly effective in preventing cancer growth and spread.
3. The Role of HIPEC in Preventing Cancer Spread
HIPEC is particularly effective in treating cancers that have spread to the peritoneal cavity, a common route for certain cancers to metastasize. By directly applying chemotherapy to the affected area, HIPEC can target microscopic cancer cells that might be present even after the visible tumors have been removed.
- Preventing Peritoneal Carcinomatosis: One of the most significant roles of HIPEC is in preventing peritoneal carcinomatosis, which occurs when cancer cells spread throughout the peritoneal cavity. By applying chemotherapy directly to this area, HIPEC aims to eliminate these cells before they can form new tumors.
- Effectiveness in Microscopic Disease: After surgical removal of large visible tumors, HIPEC targets residual microscopic disease that might have been missed. This significantly reduces the likelihood of cancer regrowth and spread in the abdominal cavity.
4. HIPEC in Treating Specific Types of Cancer
HIPEC has been used to treat several types of cancer, particularly those that affect the abdominal organs. Some of the cancers most commonly treated with HIPEC include:
- Colorectal Cancer: Colorectal cancer can spread to the peritoneal cavity in its later stages. HIPEC has shown promise in reducing the risk of recurrence and prolonging survival for patients with peritoneal metastases from colorectal cancer.
- Ovarian Cancer: Ovarian cancer often spreads to the peritoneal cavity, and HIPEC has been shown to improve survival in patients with peritoneal metastases from ovarian cancer.
- Gastric Cancer: Gastric cancer, when diagnosed at advanced stages, can spread to the peritoneum. HIPEC can help to treat this metastasis, improving patient outcomes.
- Appendiceal Cancer: HIPEC is also widely used in treating appendiceal cancer, especially in patients with pseudomyxoma peritonei, where mucin-producing cells spread throughout the peritoneal cavity.
5. Clinical Outcomes and Effectiveness
Several clinical studies and trials have assessed the effectiveness of HIPEC in cancer treatment. While it has shown promising results, the overall success of HIPEC depends on various factors such as the type and stage of cancer, the extent of metastasis, and the patient’s overall health.
- Survival Rates: Studies have shown that HIPEC, especially when combined with cytoreductive surgery (the removal of as much tumor tissue as possible), can significantly improve survival rates in patients with peritoneal metastases. For example, patients with peritoneal carcinomatosis from colorectal cancer have seen improved survival outcomes when treated with HIPEC compared to traditional chemotherapy alone.
- Recurrence Prevention: HIPEC helps in reducing the chances of recurrence by targeting residual microscopic cancer cells that might otherwise evade detection and cause a relapse.
However, the success rate is not universal, and HIPEC may not be appropriate for all patients. For patients with cancers that have spread beyond the peritoneum or those who have a high tumor burden, HIPEC may not be as effective.
6. Side Effects and Risks of HIPEC
While HIPEC is a promising treatment, it is not without its risks. The procedure can cause certain side effects, including:
- Infection Risk: As with any surgery, HIPEC carries a risk of infection, especially because it involves opening the abdominal cavity.
- Bowel Complications: Since HIPEC involves chemotherapy treatment directly in the abdomen, there is a risk of bowel injury or dysfunction.
- Electrolyte Imbalance: The heat and chemotherapy can affect the balance of electrolytes in the body, requiring close monitoring during and after the procedure.
- Blood Clots: Patients undergoing HIPEC may be at increased risk for blood clots, especially in the post-operative period.
Despite these potential risks, many patients experience positive outcomes and long-term survival when the procedure is appropriate for their cancer type and stage.
7. The Future of HIPEC: Advancements and Research
Ongoing research continues to explore the potential of HIPEC in treating various types of cancer. New drug formulations, enhanced delivery methods, and better heat management techniques are being investigated to further improve the effectiveness of HIPEC and reduce its side effects.
There is also interest in combining HIPEC with other cancer treatments, such as immunotherapy and targeted therapy, to improve outcomes for patients with advanced cancer.
8.The Role of HIPEC in Cancer Treatment
HIPEC represents a significant advancement in cancer treatment, offering a promising option for patients with peritoneal metastases. By delivering heated chemotherapy directly to the site of the cancer, HIPEC has the potential to prevent the spread of cancer, reduce recurrence, and significantly improve survival rates for patients. While it may not be suitable for everyone, for those with certain types of abdominal cancers, HIPEC can be a life-saving procedure that offers hope for a better quality of life and extended survival.
As research into HIPEC continues to evolve, the potential for this treatment to revolutionize cancer care in the abdominal region becomes increasingly likely, providing new avenues of treatment for patients who may have limited options otherwise.