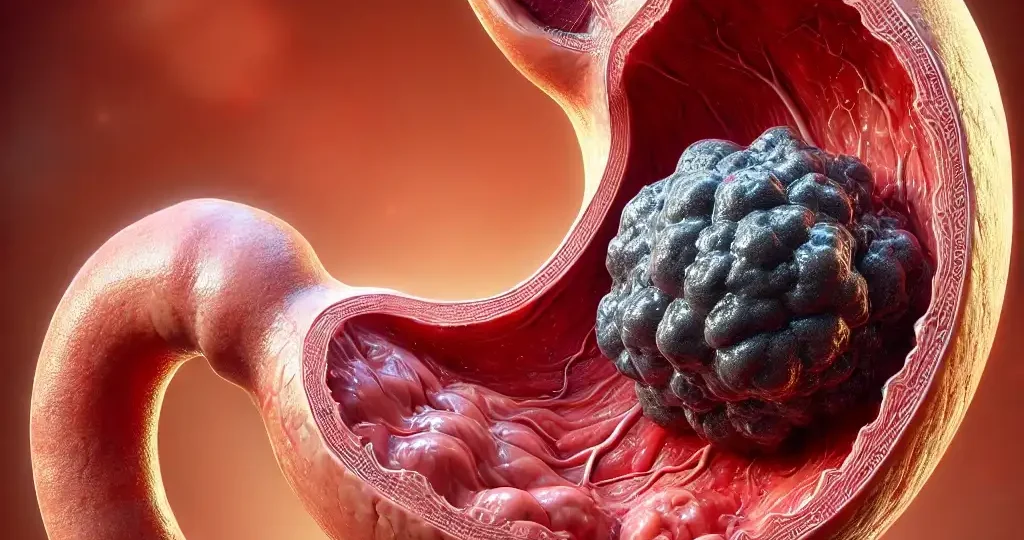
The Connection Between Diet and Stomach Cancer
Dietary habits have a profound effect on many aspects of health, including the risk of cancer. The link between nutrition and cancer has been extensively studied, revealing that certain foods and dietary practices can increase the risk of cancer, while others can help protect the body from the disease. Specifically, when it comes to stomach cancer, the type of food consumed, how food is prepared, and eating patterns all influence the risk of developing the disease.
Stomach cancer typically develops in the cells of the stomach lining and progresses over several years. Risk factors for stomach cancer include genetic predisposition, infections (such as Helicobacter pylori), and environmental factors like smoking and alcohol consumption. However, diet plays a crucial role in the development of this disease, as certain foods and nutrients can either protect against or promote the growth of cancerous cells in the stomach lining.
Risk Factors and Dietary Habits That Can Increase the Risk of Stomach Cancer
Several dietary habits and food choices have been identified as risk factors for stomach cancer. These habits often include consuming large quantities of foods that are high in salt, preservatives, or fats, and insufficient intake of fruits, vegetables, and fiber. The following are some of the key dietary factors linked to an increased risk of gastric cancer:
1. High Salt Intake
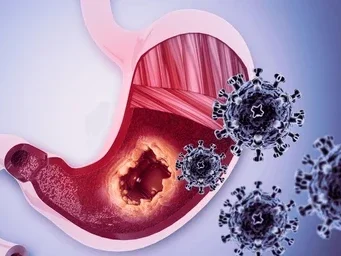
High salt consumption has long been associated with an increased risk of various types of cancer, particularly stomach cancer. Salt has been shown to damage the stomach lining, leading to inflammation and potential changes in cell behavior. Furthermore, high salt intake increases the likelihood of developing Helicobacter pylori infections, which are a major contributor to stomach cancer.
Mechanism: Excessive salt can irritate the stomach lining, causing it to become more susceptible to damage from carcinogenic compounds found in food, as well as from harmful bacteria. Studies have also shown that salt can promote the formation of cancer-causing nitrosamines in the stomach, compounds that are known to damage cells and promote cancer growth.
Sources of Salt:
- Processed meats (e.g., bacon, sausages, ham)
- Canned soups and vegetables
- Fast food
- Snack foods (e.g., chips, pretzels)
- Salty condiments (e.g., soy sauce, pickles)
2. Consumption of Processed and Red Meat
A diet rich in processed meats and red meats has been strongly linked to an increased risk of gastric cancer. Processed meats, such as bacon, sausages, and hot dogs, contain preservatives such as nitrates and nitrites, which can form carcinogenic substances when consumed.
Mechanism: Processed meats contain high levels of sodium and nitrates, which can create harmful compounds in the stomach. These compounds may damage the stomach lining and lead to cellular changes that increase the likelihood of cancer development. Additionally, red meat, when consumed in large quantities, can contribute to the production of harmful substances that irritate the stomach.
Sources of Processed and Red Meats:
- Sausages
- Bacon
- Hot dogs
- Deli meats
- Beef, pork, and lamb
3. Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol consumption is another dietary factor associated with an increased risk of stomach cancer, particularly when consumed in large quantities over a prolonged period. While moderate alcohol consumption may have some health benefits, excessive drinking is a known carcinogen and can lead to a variety of health problems, including stomach cancer.
Mechanism: Alcohol can irritate the stomach lining, causing inflammation and increasing the permeability of the stomach lining to harmful substances. Furthermore, alcohol consumption can alter the body’s ability to process and metabolize other carcinogenic substances, such as those found in processed foods and smoking.
Sources of Alcohol:
- Beer
- Wine
- Spirits (e.g., vodka, whiskey)
- Liquors and cocktails
4. Low Intake of Fruits and Vegetables
Fruits and vegetables are rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that help protect the body against oxidative stress and inflammation. A diet low in these essential nutrients can lead to deficiencies that may increase the risk of gastric cancer.
Mechanism: Fruits and vegetables contain phytochemicals such as flavonoids, carotenoids, and polyphenols that help neutralize free radicals and prevent DNA damage. A diet high in fruits and vegetables has been associated with a lower risk of stomach cancer because these foods promote a healthy stomach lining and help combat oxidative damage.
Examples of Beneficial Fruits and Vegetables:
- Leafy greens (e.g., spinach, kale, lettuce)
- Citrus fruits (e.g., oranges, lemons)
- Berries (e.g., strawberries, blueberries)
- Cruciferous vegetables (e.g., broccoli, cabbage, cauliflower)
5. Smoking and Dietary Factors
While smoking is a well-known risk factor for stomach cancer, when combined with poor dietary habits, the risk of developing gastric cancer increases significantly. Smoking causes direct damage to the stomach lining and reduces the body’s ability to absorb essential nutrients, which can contribute to cancer risk.
Mechanism: Smoking introduces harmful chemicals into the body, which can damage the stomach lining and increase the risk of developing ulcers and gastritis, both of which can lead to stomach cancer. Additionally, smoking may impair the body’s ability to metabolize certain foods, increasing the likelihood of harmful substances accumulating in the stomach.
Recommendations for Avoiding Risk Factors:
- Avoid processed meats and high-salt foods.
- Limit alcohol intake and practice moderation.
- Increase the consumption of fresh fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Quit smoking or avoid tobacco products.
Protective Dietary Habits: How to Reduce the Risk of Stomach Cancer
While certain dietary habits increase the risk of stomach cancer, other habits can help reduce the risk. Adopting a balanced, nutrient-rich diet that includes cancer-fighting foods and avoids harmful substances is one of the most effective ways to lower your chances of developing stomach cancer.
1. Eating More Fiber-Rich Foods
A high-fiber diet has been linked to a reduced risk of several types of cancer, including stomach cancer. Fiber helps to promote a healthy digestive system by facilitating regular bowel movements, preventing constipation, and reducing inflammation in the gut.
Sources of Fiber:
- Whole grains (e.g., brown rice, oats, quinoa)
- Legumes (e.g., lentils, beans, peas)
- Fruits and vegetables with skin (e.g., apples, berries, carrots)
- Nuts and seeds (e.g., almonds, chia seeds, flaxseeds)
2. Incorporating Antioxidant-Rich Foods
Antioxidants are compounds found in a variety of foods that help neutralize harmful free radicals in the body, which can damage cells and lead to cancer. Including antioxidant-rich foods in your diet can help reduce oxidative stress and protect the stomach lining from damage.
Examples of Antioxidant-Rich Foods:
- Berries (e.g., blueberries, raspberries)
- Dark leafy greens (e.g., kale, spinach)
- Tomatoes (rich in lycopene)
- Green tea (rich in polyphenols)
3. Increased Intake of Cruciferous Vegetables
Cruciferous vegetables are particularly beneficial for cancer prevention. These vegetables contain glucosinolates, which are compounds that have been shown to possess anti-cancer properties by promoting the detoxification of harmful substances and preventing DNA damage.
Cruciferous Vegetables:
- Broccoli
- Cabbage
- Kale
- Cauliflower
- Brussels sprouts
4. Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of several types of cancer, including stomach cancer. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help lower the risk.
Healthy Weight Maintenance Tips:
- Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise each week.
- Eat a balanced diet with whole foods, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Limit processed and high-calorie foods that contribute to weight gain.
Dietary habits play a crucial role in the development and prevention of stomach cancer. While certain foods and eating practices can increase the risk of this deadly disease, others can help protect the stomach lining and reduce cancer risk. By adopting a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fiber, while avoiding excessive salt, processed meats, and alcohol, individuals can significantly lower their risk of stomach cancer. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight and staying physically active further contributes to cancer prevention.
Ultimately, the key to reducing stomach cancer risk lies in making informed dietary choices, leading a healthy lifestyle, and seeking regular medical check-ups to catch any potential issues early.