The Link Between Allergies and the Esophagus
Allergic reactions occur when the immune system mistakenly identifies harmless substances—such as pollen, dust, or certain foods—as harmful invaders. In response, the immune system releases chemicals like histamine that trigger inflammatory responses. While most allergic reactions are commonly associated with symptoms in the skin, nose, and lungs, the digestive system—including the esophagus—can also be affected.
There are several mechanisms through which allergic reactions can impact the esophagus:
1. Allergic Esophagitis
Allergic esophagitis is an inflammation of the esophagus caused by an allergic reaction to food or environmental allergens. It is often seen in individuals with a history of atopic conditions such as asthma, eczema, or allergic rhinitis. The inflammation occurs when the immune system overreacts to an allergen, leading to the production of inflammatory cells in the esophageal lining.
Symptoms of allergic esophagitis can include:
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Heartburn or acid reflux
- Regurgitation of food
- A sensation of food being stuck in the throat
The underlying cause of allergic esophagitis is typically an allergic response to foods like dairy, wheat, soy, peanuts, or shellfish. In some cases, environmental allergens such as pollen or dust mites can also trigger an allergic reaction in the esophagus.
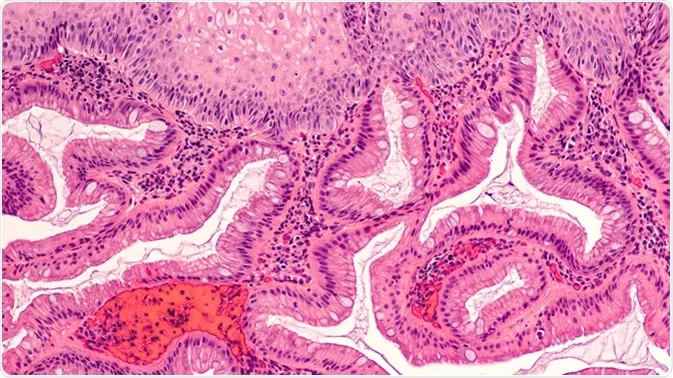
2. Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE)
Eosinophilic esophagitis is a specific type of allergic reaction that affects the esophagus, resulting in inflammation and the accumulation of eosinophils—a type of white blood cell—within the esophageal lining. EoE is often triggered by food allergens, but environmental allergens can also contribute to the condition.
Eosinophilic esophagitis is characterized by symptoms such as:
- Difficulty swallowing
- Food impaction (food getting stuck in the esophagus)
- Chronic heartburn or acid reflux
- Chest pain
- Weight loss or poor growth in children
In EoE, the eosinophils accumulate in the esophagus in response to an allergen, causing inflammation and scarring. Over time, this can lead to narrowing (stricture) of the esophagus, which can make swallowing even more difficult.
3. Oral Allergy Syndrome (OAS) and Esophageal Involvement
Oral Allergy Syndrome (OAS), also known as pollen-food syndrome, is a condition where individuals with pollen allergies experience allergic reactions to certain raw fruits, vegetables, and nuts. The proteins in these foods resemble those found in pollen, triggering an allergic response in the mouth and throat. While OAS typically causes symptoms like itching and swelling in the mouth and throat, in some cases, it can also affect the esophagus.
Individuals with OAS may experience:
- Itching or swelling in the mouth, throat, and sometimes the esophagus
- Difficulty swallowing
- A sensation of tightness or discomfort in the throat
Although OAS primarily affects the oral cavity, in some individuals, the allergic reaction can extend to the esophagus, causing inflammation and discomfort. This can result in dysphagia and other digestive symptoms.
4. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) and Allergies
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a condition where stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus, leading to irritation and inflammation. While GERD is typically associated with lifestyle factors such as obesity or a high-fat diet, allergies can exacerbate GERD symptoms or even contribute to the development of the condition.
People with allergies, particularly respiratory allergies (such as asthma or allergic rhinitis), may experience worsening of GERD symptoms. This is because allergens can trigger inflammation and swelling in the airways, leading to increased pressure on the stomach and LES. This can result in acid reflux, which may further irritate the esophagus and contribute to chronic esophageal discomfort.
Additionally, individuals with allergic conditions may have a more sensitive esophagus, making it more susceptible to acid reflux and other irritants. Managing both allergies and GERD can improve esophageal health and alleviate symptoms.
5. Food Allergies and Esophageal Reactions
Food allergies can directly impact the esophagus, especially in individuals who have an allergic reaction to certain foods. These reactions can cause swelling, inflammation, and discomfort in the esophagus. In some cases, food allergies can lead to anaphylaxis, a severe and potentially life-threatening reaction that can result in difficulty swallowing, breathing, and swallowing.
Common food allergens that can affect the esophagus include:
- Dairy products
- Eggs
- Peanuts and tree nuts
- Shellfish
- Wheat
- Soy
For individuals with food allergies, avoiding trigger foods is essential to prevent allergic reactions and protect the esophagus from further damage.
Symptoms of Esophageal Involvement in Allergic Reactions
The symptoms of esophageal involvement in allergic reactions can vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the allergy. Common symptoms include:
- Dysphagia (Difficulty Swallowing): Inflammation of the esophagus can make it difficult for food and liquids to pass through, causing a sensation of food being stuck or tightness in the chest.
- Heartburn and Acid Reflux: Allergies can trigger symptoms of heartburn, as inflammation and swelling can weaken the lower esophageal sphincter, allowing stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus.
- Regurgitation: Some people may experience regurgitation of food, especially if allergic reactions lead to narrowing or stricture of the esophagus.
- Chest Pain or Discomfort: The inflammation caused by allergies can lead to a sensation of chest pain, which may be mistaken for heart-related issues.
- Persistent Coughing or Throat Irritation: Chronic throat irritation due to allergies can lead to coughing or a sore throat, especially if the allergy is affecting the upper respiratory tract.
Treatment and Management of Esophageal Symptoms Due to Allergies
Managing esophageal symptoms caused by allergic reactions involves both treating the underlying allergy and addressing the esophageal inflammation. Here are some common treatment strategies:
1. Identifying and Avoiding Allergens
The most effective way to manage allergic reactions affecting the esophagus is to identify and avoid the allergens that trigger the response. This may involve working with an allergist to undergo testing to determine specific food or environmental allergens.
2. Anti-Inflammatory Medications
For individuals with allergic esophagitis or eosinophilic esophagitis, anti-inflammatory medications such as corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and swelling in the esophagus. These medications can help alleviate symptoms and prevent further damage to the esophageal lining.
3. Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs)
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are commonly prescribed for individuals with GERD and esophageal inflammation. These medications reduce stomach acid production, which can help prevent acid reflux and relieve symptoms of heartburn.
4. Dietary Modifications
For individuals with food allergies, avoiding trigger foods is essential. A food elimination diet may be recommended to identify specific allergens. In cases of eosinophilic esophagitis, certain foods may need to be removed from the diet to reduce inflammation.
5. Immunotherapy and Allergy Treatments
For people with environmental allergies, such as pollen or dust mites, immunotherapy (allergy shots) may be recommended to desensitize the immune system to allergens. This can help reduce allergic responses in the esophagus and other parts of the body.
Allergic reactions can have a significant impact on the esophagus, leading to conditions such as allergic esophagitis, eosinophilic esophagitis, and GERD. The symptoms of these conditions—such as difficulty swallowing, chest pain, and heartburn—can be uncomfortable and disruptive to daily life. Fortunately, there are effective ways to manage and treat esophageal symptoms caused by allergies, including avoiding allergens, taking anti-inflammatory medications, and making dietary modifications.