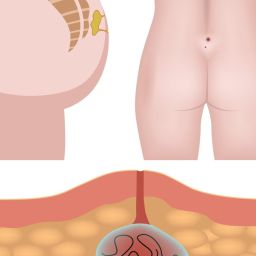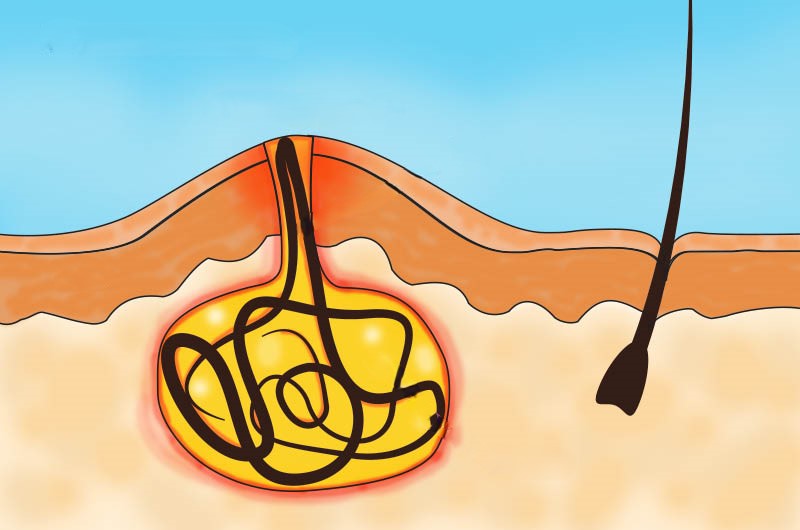
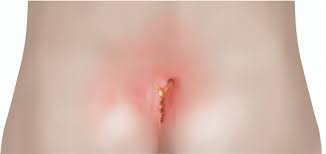
Natural Solutions for Pain Relief in Pilonidal Sinus
While medical treatment is often necessary to address pilonidal sinus, several natural remedies can provide relief from pain and inflammation. These approaches are typically aimed at reducing inflammation, soothing discomfort, and preventing further irritation.
1. Warm Sitz Baths
One of the simplest and most effective methods to relieve pilonidal sinus pain is taking warm sitz baths. A sitz bath involves sitting in warm water for 15 to 20 minutes, which helps to relax the muscles in the affected area, reduce inflammation, and promote blood circulation.
How to Use:
- Fill a bathtub or basin with warm water.
- Soak the affected area for at least 15-20 minutes, ensuring the water covers the tailbone area.
- For added relief, you may use Epsom salts, which have anti-inflammatory properties.
Sitz baths are especially helpful when there is tenderness or swelling around the sinus. They should be done twice a day to keep the area clean and to manage discomfort.
2. Cold Compresses
Cold compresses are another natural remedy to manage the swelling and pain associated with pilonidal sinus. The cold temperature helps reduce blood flow to the area, minimizing inflammation and providing immediate pain relief.
How to Use:
- Wrap some ice in a cloth or use a cold pack.
- Apply it to the affected area for 10–15 minutes several times a day.
- Do not apply ice directly to the skin to avoid frostbite.
Cold compresses are particularly beneficial during flare-ups or when an abscess forms, helping to reduce pressure and alleviate pain.
3. Essential Oils
Essential oils like tea tree oil, eucalyptus oil, and lavender oil are well-known for their antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties. These oils can help soothe the skin, reduce inflammation, and prevent bacterial infection around the pilonidal sinus.
How to Use:
- Mix a few drops of essential oil with a carrier oil (e.g., coconut oil or olive oil).
- Apply it to the affected area once or twice a day.
- Alternatively, you can add a few drops of essential oil to your sitz bath.
Be cautious when applying essential oils, as they should never be used undiluted on the skin, as they can cause irritation. Always test a small amount on the skin before full application.
4. Turmeric and Ginger
Turmeric and ginger are natural anti-inflammatory agents that can help reduce pain and swelling in pilonidal sinus. Turmeric contains curcumin, a compound with powerful anti-inflammatory properties, while ginger helps reduce pain and promotes circulation.
How to Use:
- You can add a teaspoon of turmeric powder to warm milk or water and drink it daily.
- Alternatively, you can make a paste by mixing turmeric powder with a small amount of water and applying it to the affected area.
- Ginger can also be consumed by drinking ginger tea or mixing ginger juice with honey.
These herbs not only help manage pain but also support the healing process by reducing inflammation in the affected area.
5. Aloe Vera
Aloe vera is renowned for its soothing properties and is often used to treat skin irritation. Its gel can help reduce inflammation and promote healing, providing comfort to individuals with pilonidal sinus.
How to Use:
- Apply fresh aloe vera gel directly to the affected area.
- Leave it on for 20-30 minutes before gently washing it off with lukewarm water.
- Repeat this process 2-3 times a day for best results.
Aloe vera also helps keep the area moisturized, which can prevent skin cracking and further irritation.
6. Proper Hygiene
Maintaining proper hygiene is critical for managing pilonidal sinus. Bacteria and debris trapped in the sinus can lead to infections, making the condition worse. Regular cleaning and care can help minimize discomfort and prevent infection.
How to Maintain Hygiene:
- Gently wash the affected area with mild soap and warm water.
- Pat the area dry with a clean towel to prevent moisture buildup, which can cause further irritation.
- Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive scrubs, as they can damage the skin and exacerbate the pain.
Additionally, keeping the area free from excess hair can help reduce the risk of ingrown hairs, which can worsen the condition.
Medical Solutions for Pilonidal Sinus Pain Relief
In more severe cases, medical intervention is often necessary to manage pilonidal sinus pain. If natural remedies fail to provide adequate relief, a healthcare provider may recommend medications, minor procedures, or even surgery to alleviate the pain and address the underlying cause.
1. Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers
Over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers such as ibuprofen (Advil) or acetaminophen (Tylenol) can help manage mild to moderate pain associated with pilonidal sinus. These medications work by reducing inflammation and blocking pain signals.
How to Use:
- Follow the instructions on the medication label to ensure proper dosage.
- Ibuprofen and acetaminophen can be taken every 4 to 6 hours, as needed, but should not exceed the maximum daily dose.
OTC pain relievers can help manage discomfort but are not a long-term solution for chronic pain.
2. Antibiotics for Infections
If a pilonidal sinus becomes infected, antibiotics are necessary to treat the infection and prevent it from spreading. Common antibiotics prescribed include cephalexin, doxycycline, and clindamycin.
How to Use:
- Antibiotics should be taken as prescribed by a doctor, and the full course should be completed even if symptoms improve.
- It is important to finish the entire treatment to prevent the infection from returning.
In some cases, if the infection is severe, a doctor may need to drain an abscess before prescribing antibiotics.
3. Incision and Drainage (I&D)
If an abscess has formed due to a pilonidal sinus infection, a minor surgical procedure called incision and drainage (I&D) may be necessary. During this procedure, the surgeon makes a small incision to drain the pus from the abscess, relieving pressure and pain.
How It Helps:
- The procedure provides immediate pain relief by removing the pus and reducing swelling.
- I&D is often done under local anesthesia, meaning the patient remains awake but the area is numbed.
While this procedure can provide significant relief, it does not address the root cause of the pilonidal sinus. There may be a recurrence of abscesses in the future.
4. Surgical Treatment
For individuals with recurrent or chronic pilonidal sinus, surgery may be required to remove the sinus and prevent future infections. There are several surgical approaches, including excision and flap surgery.
Excision Surgery:
- The sinus and surrounding tissue are surgically removed to prevent recurrence.
- The area is then sutured closed.
Flap Surgery:
- In cases where excision leaves a large wound, flap surgery involves using healthy tissue to close the wound and promote faster healing.
Post-Surgical Care:
- Pain management after surgery is essential and typically involves stronger pain relievers, including prescription medications.
- Sitz baths and other comfort measures are recommended during recovery.
Surgical options are typically recommended when other treatments have failed or if the pilonidal sinus is recurrent and problematic.
Prevention of Pilonidal Sinus Pain and Recurrence
Once pain from pilonidal sinus has been managed, it is important to take steps to prevent future occurrences. Some effective strategies for preventing recurrence include:
- Maintaining hygiene to keep the area clean and free from bacteria.
- Managing weight to reduce pressure on the tailbone and surrounding area.
- Shaving or waxing the hair in the region to prevent ingrown hairs.
- Avoiding prolonged sitting on hard surfaces to reduce pressure.
By following these preventive measures, patients can reduce the risk of recurrence and manage pilonidal sinus pain effectively.
Managing pilonidal sinus pain requires a comprehensive approach that includes both natural remedies and medical treatments. Natural solutions, such as warm sitz baths, cold compresses, and essential oils, can provide immediate relief and help manage inflammation. However, when the condition is more severe or infections develop, medical treatments like antibiotics, incision and drainage, or surgery may be necessary.