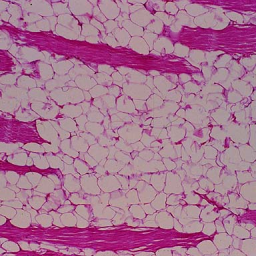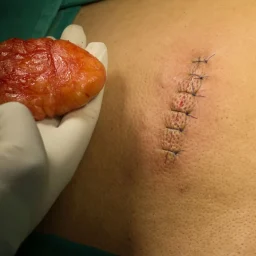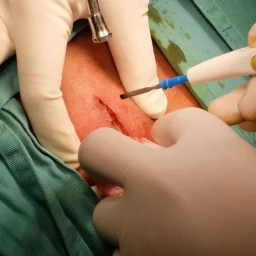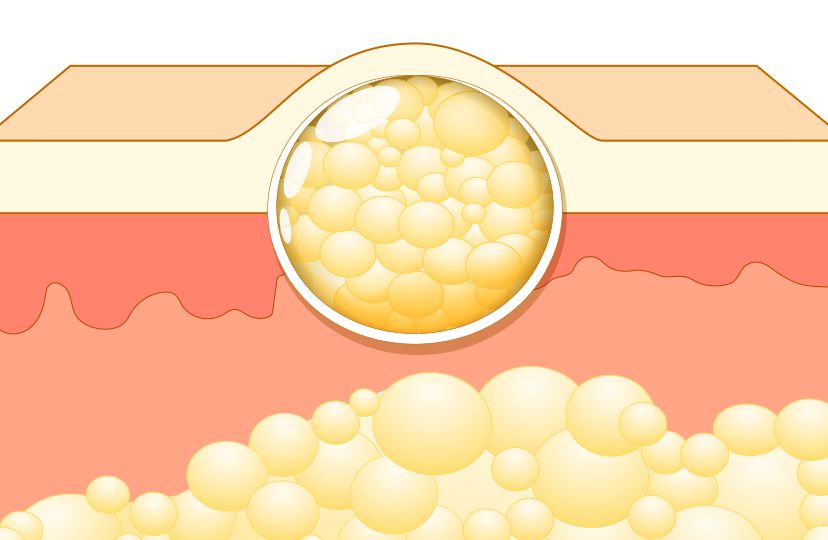
1. The Role of Nutrition in Lipoma Growth and Management
While there is no direct link between specific foods and the formation of lipomas, certain dietary habits can influence fat accumulation in the body. Lipomas are made of fatty tissue, and being overweight or obese is a known risk factor for the formation of lipomas. Maintaining a healthy body weight and a balanced diet can prevent excess fat buildup and reduce the chances of developing new lipomas or exacerbating existing ones.
Healthy Fats vs. Unhealthy Fats
It is essential to distinguish between healthy and unhealthy fats in the diet. Healthy fats, found in foods like avocados, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish, provide essential fatty acids that promote overall health. These fats are important for heart health, hormone regulation, and skin health. On the other hand, unhealthy fats, especially trans fats and excessive saturated fats, can contribute to weight gain and the development of abdominal fat.
People with abdominal lipomas should focus on incorporating more unsaturated fats (e.g., olive oil, flaxseeds, and nuts) into their diet while limiting processed foods high in unhealthy fats. This dietary approach helps maintain a healthy weight and can contribute to better management of existing lipomas.
The Importance of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, as well as in flaxseeds and walnuts, offer anti-inflammatory benefits. These healthy fats may help reduce the inflammation that can accompany lipomas, especially if they become larger or painful. Omega-3s may also help reduce overall body fat, potentially decreasing the likelihood of new lipomas developing.
2. High-Quality Protein Intake
Protein plays a critical role in building and repairing tissues, including muscle and skin. For individuals with lipomas, ensuring an adequate intake of protein can help maintain lean muscle mass, reduce excess fat storage, and promote overall metabolic health. Consuming lean protein sources helps support healthy weight management, which is essential for controlling the size and number of lipomas.
Lean Protein Sources
Incorporate lean protein sources such as:
- Chicken breast
- Turkey
- Tofu and tempeh (for plant-based diets)
- Legumes and beans
- Low-fat dairy products like yogurt and cottage cheese
Protein can also promote satiety, helping to curb overeating and maintain a healthy weight.
3. Fiber-Rich Foods for Weight Management
A diet rich in fiber is crucial for maintaining a healthy weight, as it helps control hunger and promotes a feeling of fullness. Additionally, fiber plays an important role in digestive health by supporting regular bowel movements, reducing bloating, and enhancing overall gut health.
Sources of Fiber
Fiber can be found in a variety of plant-based foods, including:
- Whole grains (e.g., brown rice, quinoa, and oats)
- Vegetables (e.g., leafy greens, broccoli, carrots)
- Fruits (e.g., apples, pears, berries)
- Legumes and beans (e.g., lentils, chickpeas)
By incorporating more fiber into the diet, individuals can support their digestive system, which in turn helps with fat metabolism and weight management, reducing the risk of excess fat storage and lipoma formation.
4. Antioxidant-Rich Foods for Overall Health
Antioxidants help protect the body from oxidative stress and inflammation, both of which may contribute to the growth of lipomas. While there is no direct evidence that antioxidants can shrink or prevent lipomas, they may help reduce the inflammation around lipomas, which can be beneficial if the growth becomes painful or uncomfortable.
Sources of Antioxidants
Foods rich in antioxidants include:
- Berries (e.g., blueberries, strawberries, raspberries)
- Leafy greens (e.g., spinach, kale)
- Nuts (e.g., almonds, walnuts)
- Dark chocolate (in moderation, with at least 70% cocoa)
- Green tea
- Brightly colored fruits and vegetables (e.g., tomatoes, peppers, oranges)
Including a variety of antioxidant-rich foods in your diet can help combat oxidative stress and may play a role in the prevention of other conditions associated with inflammation.
5. Limiting Processed and Sugary Foods
One of the most important dietary changes for people living with lipomas is reducing the intake of processed and sugary foods. High sugar and refined carbohydrates contribute to weight gain, insulin resistance, and fat accumulation, which are known risk factors for lipoma development.
Effects of Sugar on Fat Storage
Excessive sugar consumption can lead to insulin spikes, promoting fat storage in the body, especially around the abdominal area. High sugar levels can also contribute to increased inflammation, which can worsen existing lipomas.
It’s essential to limit processed snacks, sugary drinks, and fast food, opting instead for whole foods that are nutrient-dense and minimally processed.
Processed Foods and Trans Fats
Processed foods often contain trans fats, which are unhealthy fats that contribute to weight gain, inflammation, and the development of lipomas. These fats can be found in foods like fried items, baked goods, and margarine. Trans fats should be avoided as much as possible, and instead, healthier fats like those from nuts, seeds, and olive oil should be used in cooking.
6. Hydration and Its Importance for Lipoma Management
Adequate hydration is vital for overall health and may also contribute to the management of lipomas. Staying hydrated helps the body function optimally by supporting the removal of toxins, improving skin health, and promoting fat metabolism.
Dehydration can impair the body’s ability to process fats and may lead to an increase in the accumulation of adipose tissue, potentially contributing to the growth of lipomas.
How Much Water Should You Drink?
It is generally recommended to drink at least 8 cups (64 ounces) of water per day, though this can vary based on individual needs, physical activity, and climate. Drinking water consistently throughout the day can help with digestion, maintain skin elasticity, and keep the body’s metabolism running efficiently.
7. Supplementing with Vitamins and Minerals
Certain vitamins and minerals may offer benefits in terms of managing lipomas. For instance, vitamin D and calcium play a role in regulating fat metabolism, while magnesium can help with muscle function and inflammation. Ensuring adequate intake of these nutrients is important for overall health and can help mitigate some of the factors that contribute to lipoma growth.
Key Vitamins and Minerals
- Vitamin D: Found in fatty fish, egg yolks, and fortified foods, vitamin D helps regulate fat metabolism and supports immune function.
- Magnesium: Sources include nuts, seeds, leafy greens, and legumes, which help reduce muscle spasms and inflammation around lipomas.
- Calcium: Dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified plant-based milk are good sources that help with muscle and fat regulation.
Healthy Eating for Managing Abdominal Lipomas
Living with abdominal lipomas doesn’t have to be overwhelming. By maintaining a healthy and balanced diet, individuals can manage their weight, reduce inflammation, and prevent the development of additional lipomas. While there is no cure for lipomas, healthy eating habits can support overall well-being, improve body composition, and reduce the likelihood of new lipomas forming. By focusing on whole, nutrient-dense foods, limiting processed and sugary foods, and staying hydrated, individuals can lead healthier lives while managing their condition effectively.
Incorporating regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, or strength training, can further enhance the results of a healthy diet, helping to manage existing lipomas and prevent future growth.